
Investigación


Refuerzo de pilares
Investigación
Punzonamiento
Investigación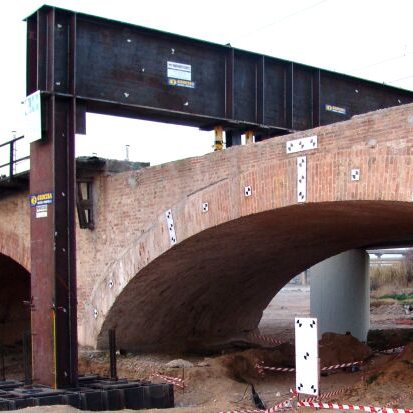
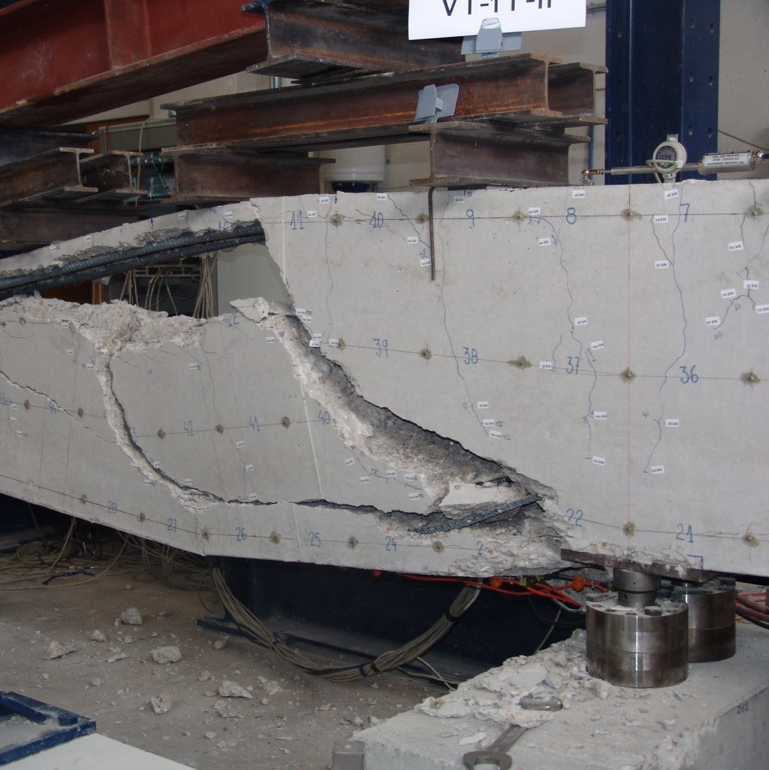
Ensayo puentes de fábrica
Investigación
Fábrica pretensada
Investigación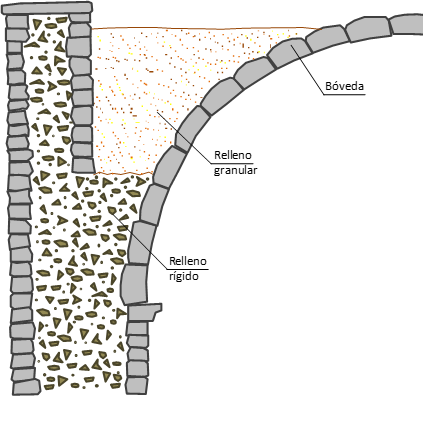
Rellenos en edificación
Investigación
Puentes espaciales
Investigación
Paneles prefabricados
Investigación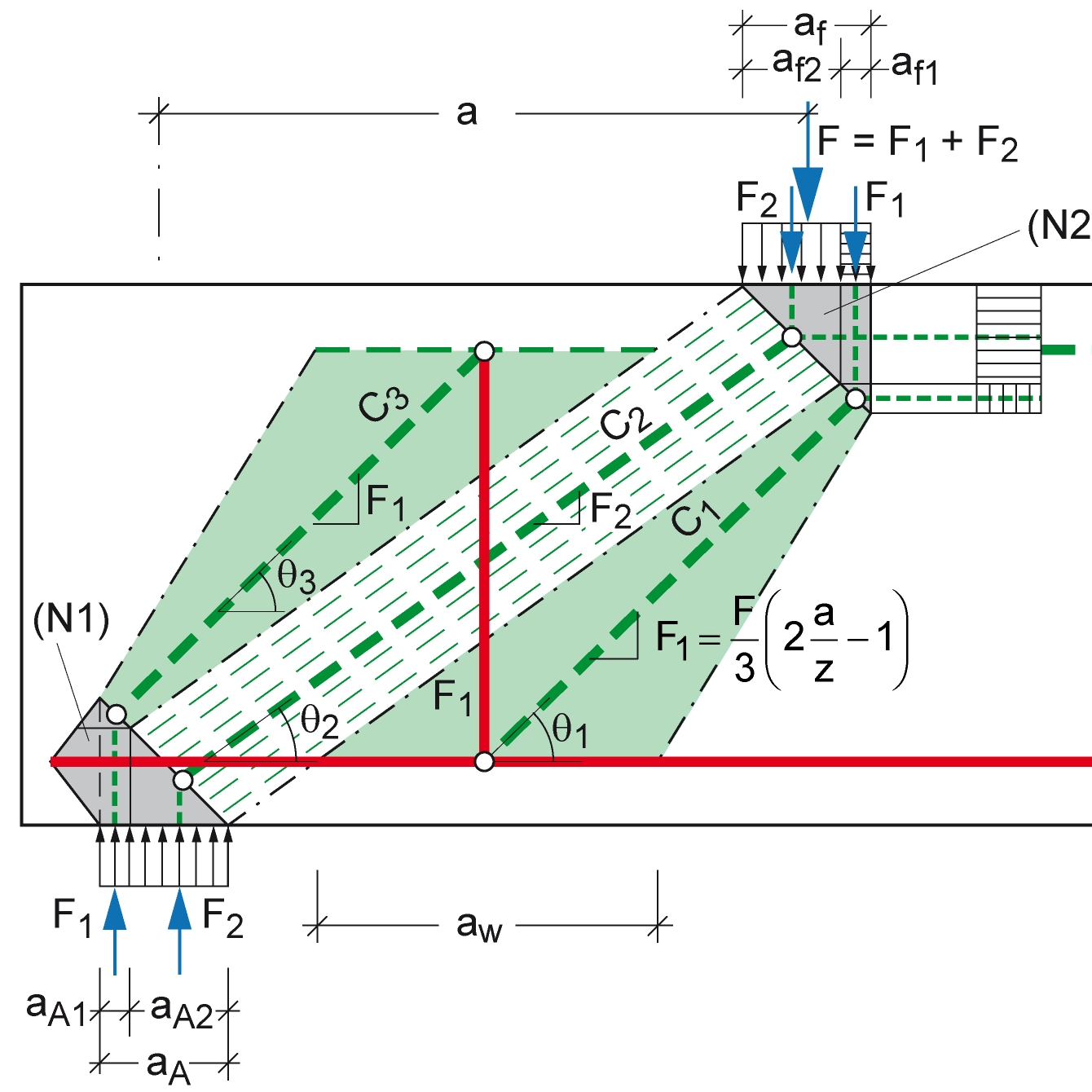
Modelos STM
Investigación
FRP recicladas
Investigación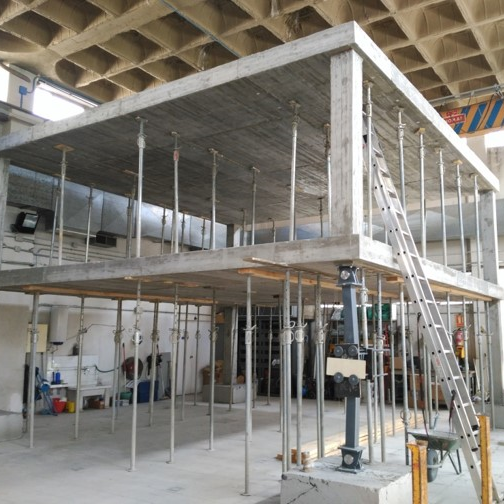
Robustness
Investigación
Acciones explosivas
Investigación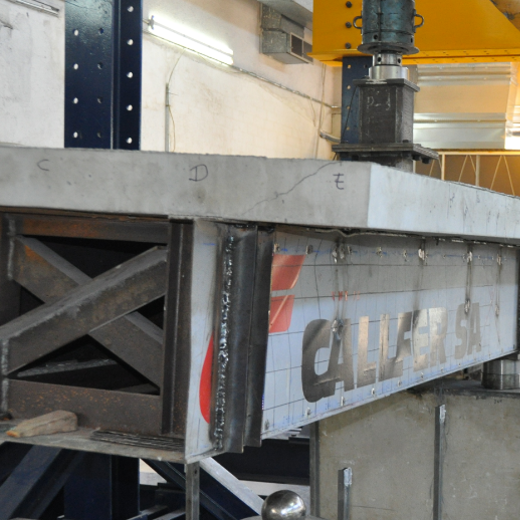
Interacción M-V-T
Investigación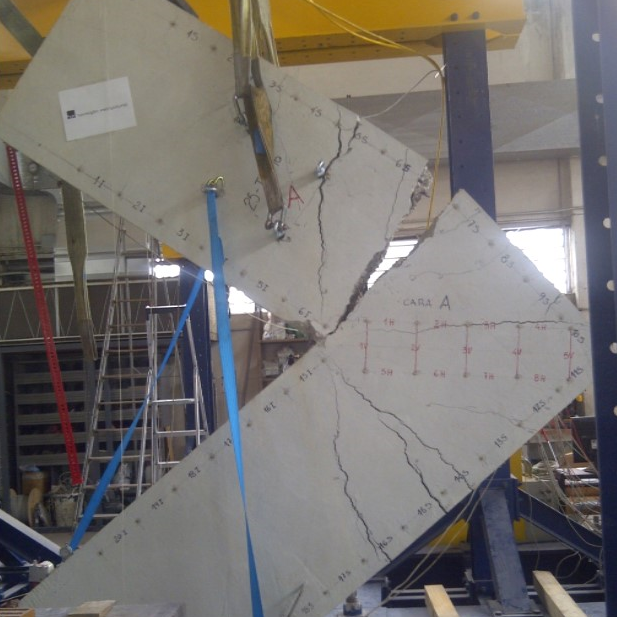
Armaduras ancladas con placas
Investigación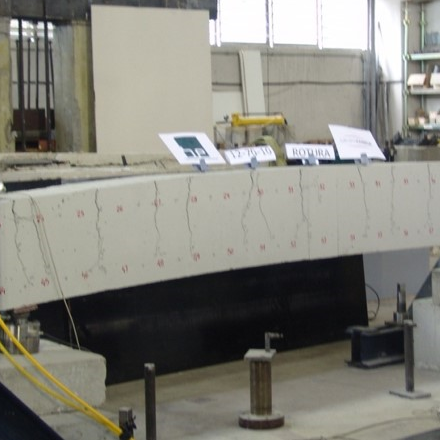
Fisuración
Investigación
Cortante estructura hiperestáticas
Investigación
Apuliabase
Investigación
Prueba carlos
InvestigaciónPublicaciones
.
2018 |
Todisco, L; Bayrak, O; Reineck, K -H ACI-DAfStb database for tests on deep beams and comparisons with code provisions Journal Article Structural Concrete, 19 (1), 2018, ISSN: 17517648. @article{Todisco2018a, title = {ACI-DAfStb database for tests on deep beams and comparisons with code provisions}, author = {L Todisco and O Bayrak and K -H Reineck}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201700061}, issn = {17517648}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {19}, number = {1}, abstract = {textcopyright 2017 fib. International Federation for Structural Concrete In an effort to calibrate design methods and code provisions, an ACI-DAfStb database was assembled for deep beams and non-slender beams with vertical stirrups and horizontal web/skin reinforcement subjected to point loads. This collection database includes 218 tests, and with the exception of a few, all tests have a shear span to effective beam depth ratios less than 2.4, that is, $kappa$ = a/d textless 2.4. For the purposes of evaluating the accuracy and conservativeness of design provisions, several control and filtering criteria were applied, and after this process, 89 beams remained in the evaluation database. In light of this database, the performance of shear design provisions of ACI 318-14 and Eurocode 2, as well as strut-and-tie models (STMs) of the FIP Recommendations were examined. The analyses conducted using this database indicated that the application of STMs of ACI 318-14 is conservative, that is, the database analyses yielded less unsafe tests than the desired 5% fractile. Furthermore, statistical evaluations showed that shear design expressions of Eurocode 2 and FIP Recommendations for non-slender beams and deep beams are conservative too.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2017 fib. International Federation for Structural Concrete In an effort to calibrate design methods and code provisions, an ACI-DAfStb database was assembled for deep beams and non-slender beams with vertical stirrups and horizontal web/skin reinforcement subjected to point loads. This collection database includes 218 tests, and with the exception of a few, all tests have a shear span to effective beam depth ratios less than 2.4, that is, $kappa$ = a/d textless 2.4. For the purposes of evaluating the accuracy and conservativeness of design provisions, several control and filtering criteria were applied, and after this process, 89 beams remained in the evaluation database. In light of this database, the performance of shear design provisions of ACI 318-14 and Eurocode 2, as well as strut-and-tie models (STMs) of the FIP Recommendations were examined. The analyses conducted using this database indicated that the application of STMs of ACI 318-14 is conservative, that is, the database analyses yielded less unsafe tests than the desired 5% fractile. Furthermore, statistical evaluations showed that shear design expressions of Eurocode 2 and FIP Recommendations for non-slender beams and deep beams are conservative too. |
Todisco, Leonardo Apuliabase: un sistema integrado de gestión del patrimonio aplicado a los Trulli Journal Article Patrimonio histórico de Castilla y León, (63), pp. 42–44, 2018. @article{todisco2018apuliabase, title = {Apuliabase: un sistema integrado de gestión del patrimonio aplicado a los Trulli}, author = {Leonardo Todisco}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-01-01}, journal = {Patrimonio histórico de Castilla y León}, number = {63}, pages = {42--44}, publisher = {Fundación del Patrimonio Histórico de Castilla y León}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Todisco, L; Stocks, E; León, J; Corres, H Enhancing the Structural Performance of Masonry Structures by Post-Tensioning Journal Article Nexus Network Journal, pp. 1–21, 2018. @article{Todisco2018b, title = {Enhancing the Structural Performance of Masonry Structures by Post-Tensioning}, author = {L Todisco and E Stocks and J León and H Corres}, doi = {10.1007/s00004-018-0374-z}, year = {2018}, date = {2018-01-01}, journal = {Nexus Network Journal}, pages = {1--21}, abstract = {textcopyright 2018 Kim Williams Books, Turin Despite the evident advantages of combining masonry with prestress, their joint use has been poorly exploited during the last decades. This paper claims the high potential of masonry as a primary load-bearing material when combined with post-tensioning. This work deals with arch footbridges and antifunicular structures. With respect to the first, this research illustrates the introduction of external loads by internal post-tensioning to favourably increase the axial forces in a masonry arch, and consequently improving its structural behaviour. With respect to the second, this work shows how bending moments in a non-funicular 2D curved geometry can be eliminated through an external post-tensioning system. In summary, this research strongly expands the range of post-tensioned masonry structures that exhibit a bending-free (or quasi bending-free) behaviour and, de facto, opens up new possibilities for designs that combine structural efficient solutions with traditional materials.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2018 Kim Williams Books, Turin Despite the evident advantages of combining masonry with prestress, their joint use has been poorly exploited during the last decades. This paper claims the high potential of masonry as a primary load-bearing material when combined with post-tensioning. This work deals with arch footbridges and antifunicular structures. With respect to the first, this research illustrates the introduction of external loads by internal post-tensioning to favourably increase the axial forces in a masonry arch, and consequently improving its structural behaviour. With respect to the second, this work shows how bending moments in a non-funicular 2D curved geometry can be eliminated through an external post-tensioning system. In summary, this research strongly expands the range of post-tensioned masonry structures that exhibit a bending-free (or quasi bending-free) behaviour and, de facto, opens up new possibilities for designs that combine structural efficient solutions with traditional materials. |
2017 |
Iasiello, C; Caldentey, A P; Groli, G Analysis of TBM Lining Rings under Lack of Gap Fill: Practical Case of Ovalization and Crack Patterns Journal Article Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 31 (4), 2017. @article{Iasiello2017, title = {Analysis of TBM Lining Rings under Lack of Gap Fill: Practical Case of Ovalization and Crack Patterns}, author = {C Iasiello and A P Caldentey and G Groli}, doi = {10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0001010}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-01-01}, journal = {Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities}, volume = {31}, number = {4}, abstract = {textcopyright 2017 American Society of Civil Engineers. This paper presents a practical approach to the study of defects in a tunnel-boring machine (TBM) ring due to the lack of gap filling during the construction phases. This lack of gap fill can produce an uncontrolled ovalization of the ring, which can lead to multicracking along the segments, in particular at the tunnel crown. After a brief description of the causes of the problem and the state of the art of ovalization in a TBM ring, a real case is analyzed considering the nonlinear moment curvature behavior of a reinforced concrete section based on the constitutive laws of the materials leading to a redistribution of internal forces. The results of this approach are compared with measured field data, in particular regarding the tunnel ovalization and the crack widths detected along the ring.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2017 American Society of Civil Engineers. This paper presents a practical approach to the study of defects in a tunnel-boring machine (TBM) ring due to the lack of gap filling during the construction phases. This lack of gap fill can produce an uncontrolled ovalization of the ring, which can lead to multicracking along the segments, in particular at the tunnel crown. After a brief description of the causes of the problem and the state of the art of ovalization in a TBM ring, a real case is analyzed considering the nonlinear moment curvature behavior of a reinforced concrete section based on the constitutive laws of the materials leading to a redistribution of internal forces. The results of this approach are compared with measured field data, in particular regarding the tunnel ovalization and the crack widths detected along the ring. |
Todisco, Leonardo; León, Javier Criterios de análisis y comprobación de estructuras de fábrica Incollection León Javier, Goicolea José M (Ed.): Los puentes de piedra (o ladrillo) antaño y hogaño., pp. 158–168, Fundación Juanelo Turriano, Madrid, 2017. @incollection{Todisco2017a, title = {Criterios de análisis y comprobación de estructuras de fábrica}, author = {Leonardo Todisco and Javier León}, editor = {Goicolea José M {León Javier}}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-01-01}, booktitle = {Los puentes de piedra (o ladrillo) antaño y hogaño.}, pages = {158--168}, publisher = {Fundación Juanelo Turriano}, address = {Madrid}, chapter = {10}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {incollection} } |
Todisco, Leonardo; Sanitate, Giuseppe; Lacorte, Giuseppe Geometry and Proportions of the Traditional Trulli of Alberobello Journal Article Nexus Network Journal, 2017, ISSN: 1590-5896. @article{Todisco2017b, title = {Geometry and Proportions of the Traditional Trulli of Alberobello}, author = {Leonardo Todisco and Giuseppe Sanitate and Giuseppe Lacorte}, url = {http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00004-016-0326-4}, doi = {10.1007/s00004-016-0326-4}, issn = {1590-5896}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-01-01}, journal = {Nexus Network Journal}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Groli, G; Caldentey, A P Improving cracking behaviour with recycled steel fibres targeting specific applications – analysis according to fib Model Code 2010 Journal Article Structural Concrete, 18 (1), pp. 29–39, 2017. @article{Groli2017a, title = {Improving cracking behaviour with recycled steel fibres targeting specific applications – analysis according to fib Model Code 2010}, author = {G Groli and A P Caldentey}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201500170}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {18}, number = {1}, pages = {29--39}, abstract = {textcopyright 2017 fib. International Federation for Structural Concrete A new and appealing mean of improving the cracking behaviour of RC elements is the combined use of rebars and fibres. Previous research has shown that steel fibres recycled from end-of-life tyres are effective for this purpose. This paper presents and discusses practical applications that would benefit from the use of this technique. Firstly, two previously published examples of crack width calculation according to fib Model Code 2010 are expanded to the case under study. These practical applications show how a fibre-reinforced concrete (FRC) with a rather poor post-peak behaviour can exhibit large improvements in cracking behaviour while being economically attractive, too. The case of jointless structures is then considered, and the improvements in terms of maximum achievable length are presented and discussed. Finally, an analysis regarding the effectiveness of this solution as a function of the reinforcement ratio is discussed for both tension and bending. The main objective of this paper is to encourage the use of recycled steel fibres as an effective and sustainable mean of dealing with cracking behaviour for specific applications.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2017 fib. International Federation for Structural Concrete A new and appealing mean of improving the cracking behaviour of RC elements is the combined use of rebars and fibres. Previous research has shown that steel fibres recycled from end-of-life tyres are effective for this purpose. This paper presents and discusses practical applications that would benefit from the use of this technique. Firstly, two previously published examples of crack width calculation according to fib Model Code 2010 are expanded to the case under study. These practical applications show how a fibre-reinforced concrete (FRC) with a rather poor post-peak behaviour can exhibit large improvements in cracking behaviour while being economically attractive, too. The case of jointless structures is then considered, and the improvements in terms of maximum achievable length are presented and discussed. Finally, an analysis regarding the effectiveness of this solution as a function of the reinforcement ratio is discussed for both tension and bending. The main objective of this paper is to encourage the use of recycled steel fibres as an effective and sustainable mean of dealing with cracking behaviour for specific applications. |
Caldentey, A P; Cembranos, J M; Peiretti, H C Slenderness limits for deflection control: A new formulation for flexural reinforced concrete elements Journal Article Structural Concrete, 18 (1), pp. 118–127, 2017. @article{Caldentey2017, title = {Slenderness limits for deflection control: A new formulation for flexural reinforced concrete elements}, author = {A P Caldentey and J M Cembranos and H C Peiretti}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201600062}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {18}, number = {1}, pages = {118--127}, abstract = {textcopyright 2017 fib. International Federation for Structural Concrete The first step in the design of a structure is the definition of the geometry. This process includes the definition of the depth of slabs and beams. The depth of a flexural member is often determined by control of deflections, which can only be checked in detail at an advanced stage of the project. In order to optimize the design process, it is therefore very important to choose well the span-to-depth ratio at the beginning. In order to achieve this task in an easy manner, a lower limit to the slenderness of the beams in terms of span divided by the effective depth is proposed in most major codes. However, current proposals are rather coarse and are not necessarily on the safe side. In this paper, a new formulation for the slenderness limits, based on the physics of the problem, is presented. This formulation includes the effect of the composition of the load (live load to total load ratio) as well as the possibility of using different limits to maximum deflection and considering different, more general, support conditions. It is therefore more complete and has a larger application field than current proposals.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2017 fib. International Federation for Structural Concrete The first step in the design of a structure is the definition of the geometry. This process includes the definition of the depth of slabs and beams. The depth of a flexural member is often determined by control of deflections, which can only be checked in detail at an advanced stage of the project. In order to optimize the design process, it is therefore very important to choose well the span-to-depth ratio at the beginning. In order to achieve this task in an easy manner, a lower limit to the slenderness of the beams in terms of span divided by the effective depth is proposed in most major codes. However, current proposals are rather coarse and are not necessarily on the safe side. In this paper, a new formulation for the slenderness limits, based on the physics of the problem, is presented. This formulation includes the effect of the composition of the load (live load to total load ratio) as well as the possibility of using different limits to maximum deflection and considering different, more general, support conditions. It is therefore more complete and has a larger application field than current proposals. |
Cervenka, V; Markova, J; Mlcoch, J; Caldentey, A P; Sajdlova, T; Sykora, M Uncertainties of crack width models Inproceedings High Tech Concrete: Where Technology and Engineering Meet - Proceedings of the 2017 fib Symposium, pp. 1653–1661, 2017, ISBN: 9783319594705. @inproceedings{Cervenka2017, title = {Uncertainties of crack width models}, author = {V Cervenka and J Markova and J Mlcoch and A P Caldentey and T Sajdlova and M Sykora}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-59471-2_190}, isbn = {9783319594705}, year = {2017}, date = {2017-01-01}, booktitle = {High Tech Concrete: Where Technology and Engineering Meet - Proceedings of the 2017 fib Symposium}, pages = {1653--1661}, abstract = {textcopyright Springer International Publishing AG 2018. Crack widths for verification of serviceability limit states can be calculated by simplified formulas provided by codes of practice or by numerical analysis based on nonlinear finite element methods. Authors performed a pilot study with the aim to develop a methodology for assessment of model uncertainty involved in the crack width analysis. Experimental data of four beams were used as a reference of real physical evidence for model validation. Two crack models were investigated, namely the model proposed by the fib Model Code 2010 and the numerical model based on fracture mechanics and finite element method. The results indicate that both models tend to underestimate the maximal crack width. The mean crack widths are well simulated by the numerical model.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } textcopyright Springer International Publishing AG 2018. Crack widths for verification of serviceability limit states can be calculated by simplified formulas provided by codes of practice or by numerical analysis based on nonlinear finite element methods. Authors performed a pilot study with the aim to develop a methodology for assessment of model uncertainty involved in the crack width analysis. Experimental data of four beams were used as a reference of real physical evidence for model validation. Two crack models were investigated, namely the model proposed by the fib Model Code 2010 and the numerical model based on fracture mechanics and finite element method. The results indicate that both models tend to underestimate the maximal crack width. The mean crack widths are well simulated by the numerical model. |
2016 |
Stucchi, F; Coelho Ungaretti, M; Fujii, G; Corres Peiretti, H; Soriano Martin, J; Doniak, S Corinthians Arena – 2014 World Cup, design and construction Journal Article Structural Concrete, 17 (5), pp. 698–709, 2016. @article{Stucchi2016, title = {Corinthians Arena – 2014 World Cup, design and construction}, author = {F Stucchi and M {Coelho Ungaretti} and G Fujii and H {Corres Peiretti} and J {Soriano Martin} and S Doniak}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201600086}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {17}, number = {5}, pages = {698--709}, abstract = {Copyright textcopyright 2016 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin This paper describes the design and construction of the concrete structures of the Corinthians Arena built for the 2014 World Cup. Due to many constraints, the structure was designed, essentially, with prefabricated structural concrete members, some specific elements were designed with structural concrete cast in situ, and some areas, with special construction problems, were designed with composite steel–concrete structures.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Copyright textcopyright 2016 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin This paper describes the design and construction of the concrete structures of the Corinthians Arena built for the 2014 World Cup. Due to many constraints, the structure was designed, essentially, with prefabricated structural concrete members, some specific elements were designed with structural concrete cast in situ, and some areas, with special construction problems, were designed with composite steel–concrete structures. |
Hernando, Javier García; Caldentey, Alejandro Perez; ñ, Freddy Ari; Peiretti, Hugo Corres Design of Slender Reinforced Concrete Bridge Columns Considering the Interaction between Columns Journal Article Structural Engineering International, 26 (1), pp. 52–61, 2016. @article{Hernando2016a, title = {Design of Slender Reinforced Concrete Bridge Columns Considering the Interaction between Columns}, author = {Javier García Hernando and Alejandro Perez Caldentey and Freddy Ari{ñ}ez Fernández and Hugo Corres Peiretti}, url = {http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/iabse/sei/2016/00000026/00000001/art00008}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, journal = {Structural Engineering International}, volume = {26}, number = {1}, pages = {52--61}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Gribniak, V; Pérez Caldentey, A; Kaklauskas, G; Rimkus, A; Sokolov, A Effect of arrangement of tensile reinforcement on flexural stiffness and cracking Journal Article Engineering Structures, 124 , pp. 418–428, 2016. @article{Gribniak2016, title = {Effect of arrangement of tensile reinforcement on flexural stiffness and cracking}, author = {V Gribniak and A {Pérez Caldentey} and G Kaklauskas and A Rimkus and A Sokolov}, doi = {10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.06.026}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, journal = {Engineering Structures}, volume = {124}, pages = {418--428}, abstract = {textcopyright 2016 Elsevier Ltd Due to the highly complex cracking behaviour of reinforced concrete structures, their design for serviceability is one of the most challenging tasks of engineering practice. Existing test data support a general inference that the deformation behaviour of concrete elements is affected by the arrangement of reinforcement in the tensile zone. Most of the current design approaches are based on the experimental data of laboratory specimens with simplified arrangement of the reinforcement. Consequently, the corresponding models are often inadequate to predict deformations and cracking of elements with non-conventional distribution of the bars. In the current study, the number of the reinforcement layers is found to correlate with the flexural stiffness. The paper also compares the crack width and crack spacing experimentally determined in the beams with different numbers of reinforcement layers. The results to some extent seem to be in conflict with the generally accepted concept relating crack widths to the cracking distances. Although the observed crack distances of the beams with three layers of bars were larger, their maximum crack openings were smaller than in the conventionally reinforced specimens with the same reinforcement ratio.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2016 Elsevier Ltd Due to the highly complex cracking behaviour of reinforced concrete structures, their design for serviceability is one of the most challenging tasks of engineering practice. Existing test data support a general inference that the deformation behaviour of concrete elements is affected by the arrangement of reinforcement in the tensile zone. Most of the current design approaches are based on the experimental data of laboratory specimens with simplified arrangement of the reinforcement. Consequently, the corresponding models are often inadequate to predict deformations and cracking of elements with non-conventional distribution of the bars. In the current study, the number of the reinforcement layers is found to correlate with the flexural stiffness. The paper also compares the crack width and crack spacing experimentally determined in the beams with different numbers of reinforcement layers. The results to some extent seem to be in conflict with the generally accepted concept relating crack widths to the cracking distances. Although the observed crack distances of the beams with three layers of bars were larger, their maximum crack openings were smaller than in the conventionally reinforced specimens with the same reinforcement ratio. |
Todisco, Leonardo; Reineck, Karl-Heinz; Bayrak, Oguzhan European design rules for point loads near supports evaluated with data from shear tests on non-slender beams with vertical stirrups Journal Article Structural Concrete, 17 (2), pp. 135–144, 2016, ISSN: 14644177. @article{Todisco2016d, title = {European design rules for point loads near supports evaluated with data from shear tests on non-slender beams with vertical stirrups}, author = {Leonardo Todisco and Karl-Heinz Reineck and Oguzhan Bayrak}, url = {http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/suco.201500089}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201500089}, issn = {14644177}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {17}, number = {2}, pages = {135--144}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Todisco, Leonardo; Mueller, Caitlin Externally post-tensioned structures : Validation through physical models Inproceedings International Conference on Structures and Architecture, pp. 1144–1151, 2016, ISBN: 9781138026513. @inproceedings{Todisco2016b, title = {Externally post-tensioned structures : Validation through physical models}, author = {Leonardo Todisco and Caitlin Mueller}, isbn = {9781138026513}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, booktitle = {International Conference on Structures and Architecture}, pages = {1144--1151}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } |
Todisco, Leonardo Funicularity and Equilibrium for High-Performance Conceptual Design PhD Thesis Technical University of Madrid, Spain, 2016. @phdthesis{Todisco2016f, title = {Funicularity and Equilibrium for High-Performance Conceptual Design}, author = {Leonardo Todisco}, url = {http://oa.upm.es/39733/}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, school = {Technical University of Madrid, Spain}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {phdthesis} } |
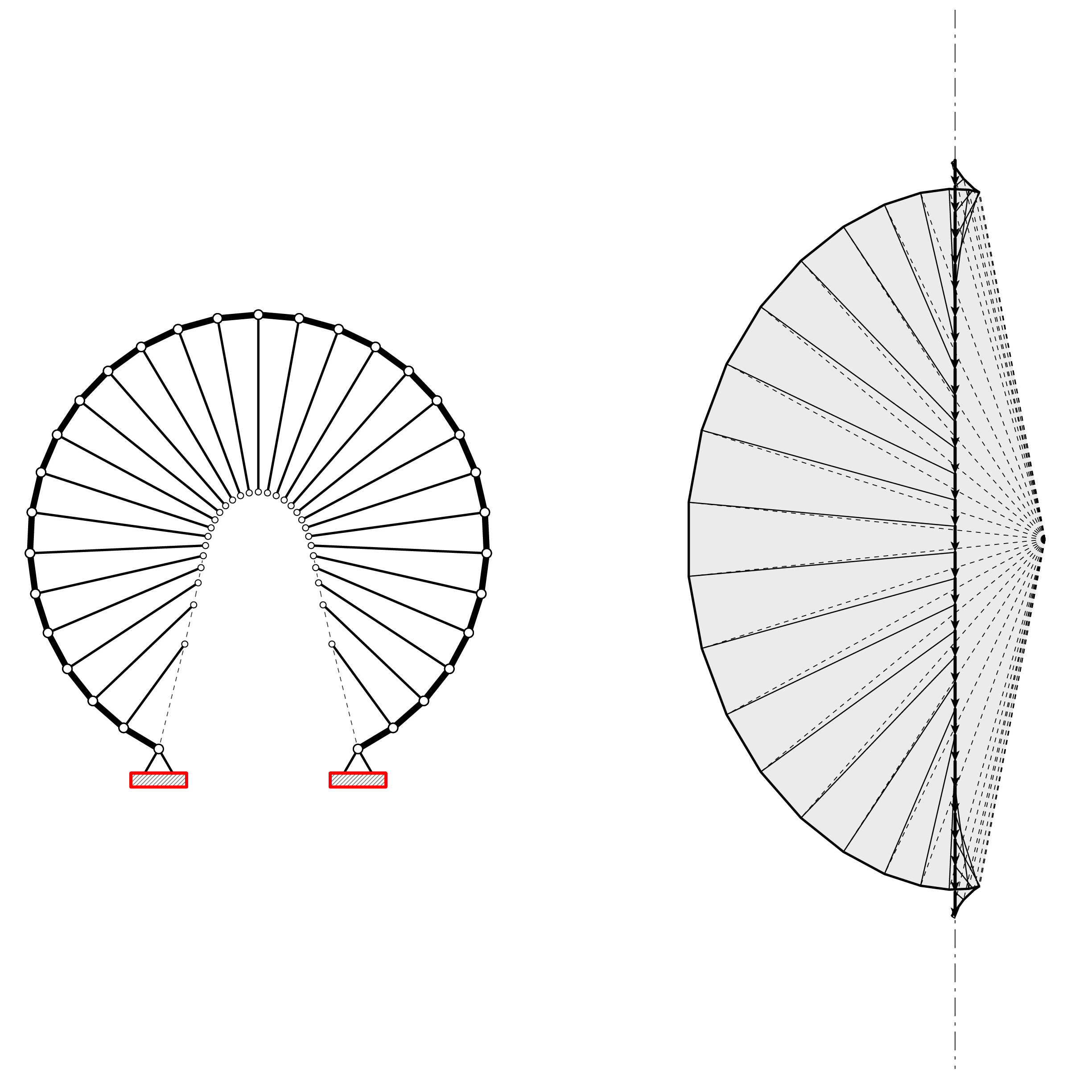
Todisco, Leonardo; Corres-Peiretti, Hugo; Mueller, Caitlin Funicularity through External Posttensioning : Design Philosophy and Computational Tool Journal Article Journal of Structural Engineering, 142 (2), pp. 1–9, 2016, ISSN: 978-90-5363-042-6. @article{Todisco2016e, title = {Funicularity through External Posttensioning : Design Philosophy and Computational Tool}, author = {Leonardo Todisco and Hugo Corres-Peiretti and Caitlin Mueller}, doi = {10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001416.}, issn = {978-90-5363-042-6}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, journal = {Journal of Structural Engineering}, volume = {142}, number = {2}, pages = {1--9}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Todisco, L; Rojo, S; Fivet, C Graphical methods for the design of masonry arches : The case of Luis Moya Blanco ' s Nuestra Señora de la Araucana in Madrid , 1972 Inproceedings International Conference on Structures and Architecture, pp. 753–759, 2016, ISBN: 9781138026513. @inproceedings{Todisco2016c, title = {Graphical methods for the design of masonry arches : The case of Luis Moya Blanco ' s Nuestra Señora de la Araucana in Madrid , 1972}, author = {L Todisco and S Rojo and C Fivet}, isbn = {9781138026513}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, booktitle = {International Conference on Structures and Architecture}, pages = {753--759}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } |
Timerman, R; Corres, H; Prieto, F; Doniak, S São vicente suspension bridge rehabilitation and cable substitution Inproceedings Maintenance, Monitoring, Safety, Risk and Resilience of Bridges and Bridge Networks - Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Bridge Maintenance, Safety and Management, IABMAS 2016, pp. 571–581, 2016, ISBN: 9781138028517. @inproceedings{Timerman2016, title = {São vicente suspension bridge rehabilitation and cable substitution}, author = {R Timerman and H Corres and F Prieto and S Doniak}, isbn = {9781138028517}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, booktitle = {Maintenance, Monitoring, Safety, Risk and Resilience of Bridges and Bridge Networks - Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Bridge Maintenance, Safety and Management, IABMAS 2016}, pages = {571--581}, abstract = {textcopyright 2016 Taylor & Francis Group, London. The São Vicente Suspension Bridge was erected in 1914 as part of the sanitation plan of the Santos and São Vicente area. Bridge condition in 2012 was deemed to be critical as some elements in trusses had disappeared and cable shown important corrosion and loss of cross section. This paper briefly describes the bridge history and the main points of the recent intervention for cable substitution and deck restoration.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } textcopyright 2016 Taylor & Francis Group, London. The São Vicente Suspension Bridge was erected in 1914 as part of the sanitation plan of the Santos and São Vicente area. Bridge condition in 2012 was deemed to be critical as some elements in trusses had disappeared and cable shown important corrosion and loss of cross section. This paper briefly describes the bridge history and the main points of the recent intervention for cable substitution and deck restoration. |
Todisco, Leonardo; Sanitate, Giuseppe Static stability of trulli Journal Article Materials and Structures, 49 (7), pp. 2893–2905, 2016, ISSN: 1359-5997. @article{Todisco2016f, title = {Static stability of trulli}, author = {Leonardo Todisco and Giuseppe Sanitate}, url = {http://link.springer.com/10.1617/s11527-015-0693-4}, doi = {10.1617/s11527-015-0693-4}, issn = {1359-5997}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, journal = {Materials and Structures}, volume = {49}, number = {7}, pages = {2893--2905}, abstract = {Trulli are remarkable examples of corbelled masonry structures commonly located in Apulia, Italy. This paper focuses on their statics. Trulli domes transfer loads in paths that follows meridians and parallels: idealization of the dome as a system of independent arches is not admissible. The aim of this research is to present a simplified methodology for assessing their stability against vertical static loads and for classifying trulli in a database in order to identify those which are in the worst conditions. The goal is achieved by adopting a static index of stability (St. I.) that takes geometry into account. The methodology has been developed within the framework of the Apuliabase Project and it has been applied to the structural vulnerability evaluation of 30 case studies. The same philosophy can be extended to other structural typologies exhibiting similar structural behaviour.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Trulli are remarkable examples of corbelled masonry structures commonly located in Apulia, Italy. This paper focuses on their statics. Trulli domes transfer loads in paths that follows meridians and parallels: idealization of the dome as a system of independent arches is not admissible. The aim of this research is to present a simplified methodology for assessing their stability against vertical static loads and for classifying trulli in a database in order to identify those which are in the worst conditions. The goal is achieved by adopting a static index of stability (St. I.) that takes geometry into account. The methodology has been developed within the framework of the Apuliabase Project and it has been applied to the structural vulnerability evaluation of 30 case studies. The same philosophy can be extended to other structural typologies exhibiting similar structural behaviour. |
Marchetto, F; ï}¿½rez Caldentey, A {P; Corres Peiretti, H Structural performance of corner joints subjected to a closing moment using mechanical anchorages: an experimental study Journal Article Structural Concrete, 17 (6), pp. 987–1002, 2016. @article{Marchetto2016, title = {Structural performance of corner joints subjected to a closing moment using mechanical anchorages: an experimental study}, author = {F Marchetto and A {P{ï}¿½rez Caldentey} and H {Corres Peiretti}}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201500222}, year = {2016}, date = {2016-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {17}, number = {6}, pages = {987--1002}, abstract = {An experimental study investigated structural performance of corner joints subjected to a closing moment using mechanical anchorages. The proposed design formulation was meant to be used when the maximum tensile force has to be anchored by the plate. In cases where a certain development length was available, the plate dimensions could be reduced, since the greater the development length, the lower was the contribution of the bearing mechanism to the total anchorage capacity. The main objective of the experimental campaign is to check whether the design of such plates was adequate for these elements and whether an element with plate-anchored reinforcement is equivalent to one with a traditional construction detail.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } An experimental study investigated structural performance of corner joints subjected to a closing moment using mechanical anchorages. The proposed design formulation was meant to be used when the maximum tensile force has to be anchored by the plate. In cases where a certain development length was available, the plate dimensions could be reduced, since the greater the development length, the lower was the contribution of the bearing mechanism to the total anchorage capacity. The main objective of the experimental campaign is to check whether the design of such plates was adequate for these elements and whether an element with plate-anchored reinforcement is equivalent to one with a traditional construction detail. |
2015 |
Todisco, Leonardo; Reineck, Karl-Heinz; Bayrak, Oguzhan Database with Shear Tests on Non-slender Reinforced Concrete Beams with Vertical Stirrups Journal Article ACI Structural Journal, 112 (6), pp. 761–770, 2015, ISSN: 0889-3241. @article{Todisco2015d, title = {Database with Shear Tests on Non-slender Reinforced Concrete Beams with Vertical Stirrups}, author = {Leonardo Todisco and Karl-Heinz Reineck and Oguzhan Bayrak}, url = {http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-84948457022&partnerID=tZOtx3y1}, doi = {10.14359/51688055}, issn = {0889-3241}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, journal = {ACI Structural Journal}, volume = {112}, number = {6}, pages = {761--770}, publisher = {American Concrete Institute}, abstract = {A database is presented with 278 tests on non-slender reinforced concrete beams with vertical stirrups. These beams are commonly referred to as non-slender beams because they have shear spandepth ratios (a/d) less than 2.4. In keeping with European terminology, the term "deep beams" is not used for these beams, because in Europe, deep beams are often defined only for ratios of a/d textless 1 and always contain vertical as well as horizontal reinforcement in their web. After having applied several control/filtering criteria, 178 beams remained in the evaluation database that can be used to check conservativeness and accuracy of relevant design provisions. For example, the application of strut-and-tie models of ACI 318-14 to non-slender beams with stirrups (and without any horizontal skin reinforcement) was unconservative-that is, it yielded database analysis results that were above the desired 5% fractile. Almost all unconservative estimations were obtained for test specimens with very low amounts of stirrups. This problem can be solved either by increasing the required amount of minimum reinforcement in the vertical direction or by placing a minimum amount of reinforcement in both the horizontal and vertical direction. It is also important to note that a comparison with Kani's shear valley showed that for a/d textless 1, the valley was not filled up to the full flexural capacity, despite the presence of vertical stirrups in test specimens.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } A database is presented with 278 tests on non-slender reinforced concrete beams with vertical stirrups. These beams are commonly referred to as non-slender beams because they have shear spandepth ratios (a/d) less than 2.4. In keeping with European terminology, the term "deep beams" is not used for these beams, because in Europe, deep beams are often defined only for ratios of a/d textless 1 and always contain vertical as well as horizontal reinforcement in their web. After having applied several control/filtering criteria, 178 beams remained in the evaluation database that can be used to check conservativeness and accuracy of relevant design provisions. For example, the application of strut-and-tie models of ACI 318-14 to non-slender beams with stirrups (and without any horizontal skin reinforcement) was unconservative-that is, it yielded database analysis results that were above the desired 5% fractile. Almost all unconservative estimations were obtained for test specimens with very low amounts of stirrups. This problem can be solved either by increasing the required amount of minimum reinforcement in the vertical direction or by placing a minimum amount of reinforcement in both the horizontal and vertical direction. It is also important to note that a comparison with Kani's shear valley showed that for a/d textless 1, the valley was not filled up to the full flexural capacity, despite the presence of vertical stirrups in test specimens. |
Todisco, L; Fivet, C; Corres-Peiretti, H; Mueller, C Design and exploration of externally posttensioned structures using graphic statics Journal Article Journal of the International Association for Shell and Spatial Structures, 56 (4), pp. 249–258, 2015. @article{Todisco2015b, title = {Design and exploration of externally posttensioned structures using graphic statics}, author = {L Todisco and C Fivet and H Corres-Peiretti and C Mueller}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, journal = {Journal of the International Association for Shell and Spatial Structures}, volume = {56}, number = {4}, pages = {249--258}, abstract = {textcopyright Copyright 2015 by Leonardo Todisco, Corentin Fivet, Hugo Corres-Peiretti and Caitlin Mueller. Funicular structures, which follow the shapes of hanging chains, work in pure tension (cables) or pure compression (arches), and offer a materially efficient solution compared to structures that work through bending action. However, the set of geometries that are funicular under common loading conditions is limited. Nonstructural design criteria, such as function, program, and aesthetics, often prohibit the selection of purely funicular shapes, resulting in large bending moments and excess material usage. In response to this issue, this paper explores the use of a new design approach that converts non-funicular planar curves into funicular shapes without changing the geometry; instead, funicularity is achieved through the introduction of new loads using external post-tensioning. The methodology is based on graphic statics, and is generalized for any twodimensional shape. The problem is indeterminate, meaning that a large range of allowable solutions is possible for one initial geometry. Each solution within this range results in different internal force distributions and horizontal reactions. The method has been implemented in an interactive parametric design environment, empowering fast exploration of diverse axial-only solutions. In addition to presenting the approach and tool, this paper provides a series of case studies and numerical comparisons between new post-tensioned structures and classical bending solutions, demonstrating that significant material can be saved without compromising on geometrical requirements.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright Copyright 2015 by Leonardo Todisco, Corentin Fivet, Hugo Corres-Peiretti and Caitlin Mueller. Funicular structures, which follow the shapes of hanging chains, work in pure tension (cables) or pure compression (arches), and offer a materially efficient solution compared to structures that work through bending action. However, the set of geometries that are funicular under common loading conditions is limited. Nonstructural design criteria, such as function, program, and aesthetics, often prohibit the selection of purely funicular shapes, resulting in large bending moments and excess material usage. In response to this issue, this paper explores the use of a new design approach that converts non-funicular planar curves into funicular shapes without changing the geometry; instead, funicularity is achieved through the introduction of new loads using external post-tensioning. The methodology is based on graphic statics, and is generalized for any twodimensional shape. The problem is indeterminate, meaning that a large range of allowable solutions is possible for one initial geometry. Each solution within this range results in different internal force distributions and horizontal reactions. The method has been implemented in an interactive parametric design environment, empowering fast exploration of diverse axial-only solutions. In addition to presenting the approach and tool, this paper provides a series of case studies and numerical comparisons between new post-tensioned structures and classical bending solutions, demonstrating that significant material can be saved without compromising on geometrical requirements. |
Bermejo, M; Santos, A P; Goicolea, J M; Pérez, A Informes de la Construccion, 67 (539), 2015. @article{Bermejo2015a, title = {Evaluation of blast loads on reinforced concrete structures with finite elements | Evaluación de acciones explosivas sobre estructuras de hormigón armado mediante elementos finitos}, author = {M Bermejo and A P Santos and J M Goicolea and A Pérez}, doi = {10.3989/ic.13.121}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, journal = {Informes de la Construccion}, volume = {67}, number = {539}, abstract = {Explosive phenomena on concrete structures have catastrophic effects in many instances despite its reduced occurrence. The civil buildings are usually not designed to withstand this type of dynamic load, so a methodology to analyze the structural response on blast loads is recommended. This paper studies the behavior of reinforced concrete frame structures against these actions by lagrangian finite elements method with explicit time integration. Finite element models of segregated concrete and rebar are used to make possible the study of structure parts as columns and slabs, but is not possible to use these detailed models in complete structures because of excessive computational costs. Shell and beam elements models properly calibrated are needed to obtain a similar response. Conclusions and practical recommendations are provided for the use and calibration of models and realistic simulations.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Explosive phenomena on concrete structures have catastrophic effects in many instances despite its reduced occurrence. The civil buildings are usually not designed to withstand this type of dynamic load, so a methodology to analyze the structural response on blast loads is recommended. This paper studies the behavior of reinforced concrete frame structures against these actions by lagrangian finite elements method with explicit time integration. Finite element models of segregated concrete and rebar are used to make possible the study of structure parts as columns and slabs, but is not possible to use these detailed models in complete structures because of excessive computational costs. Shell and beam elements models properly calibrated are needed to obtain a similar response. Conclusions and practical recommendations are provided for the use and calibration of models and realistic simulations. |
Groli, G; Pérez Caldentey, A; Marchetto, F; ñ}ez Fernández, {Arí F Serviceability performance of FRC columns under imposed displacements: An experimental study Journal Article Engineering Structures, 101 , pp. 450–464, 2015. @article{Groli2015a, title = {Serviceability performance of FRC columns under imposed displacements: An experimental study}, author = {G Groli and A {Pérez Caldentey} and F Marchetto and F {Arí{ñ}ez Fernández}}, doi = {10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.07.035}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, journal = {Engineering Structures}, volume = {101}, pages = {450--464}, abstract = {textcopyright 2015 Elsevier Ltd. This paper presents an experimental campaign aiming to explore the serviceability behaviour of columns of jointless structures reinforced with both conventional rebars and steel fibres recycled from end-of-life tyres. The test set-up is first introduced, involving columns with different reinforcement ratios, squashing load ratios and recycled fibre content. The characteristics, constructability and performance of recycled fibres are discussed. Then the results of the tests are presented and compared with non-fibre reinforced columns, showing improvements in cracking performance. Also, a simplified method of analysis has been compared to experimental results, showing good agreement in the imposed displacement vs. rebar stress behaviour. The main objective of this investigation is to encourage the use of jointless structures by presenting an appealing and sustainable technique to overcome problems such as excessive cracking.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2015 Elsevier Ltd. This paper presents an experimental campaign aiming to explore the serviceability behaviour of columns of jointless structures reinforced with both conventional rebars and steel fibres recycled from end-of-life tyres. The test set-up is first introduced, involving columns with different reinforcement ratios, squashing load ratios and recycled fibre content. The characteristics, constructability and performance of recycled fibres are discussed. Then the results of the tests are presented and compared with non-fibre reinforced columns, showing improvements in cracking performance. Also, a simplified method of analysis has been compared to experimental results, showing good agreement in the imposed displacement vs. rebar stress behaviour. The main objective of this investigation is to encourage the use of jointless structures by presenting an appealing and sustainable technique to overcome problems such as excessive cracking. |
Romo, J Conceptual design and aesthetic of bridges Conference IABSE Conference, Nara 2015: Elegance in Structures - Report, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2015, ISBN: 9783857481383. @conference{Romo201548, title = {Conceptual design and aesthetic of bridges}, author = {J Romo}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84971215722&partnerID=40&md5=54fb8c06d136dbe746c353b690f16981}, isbn = {9783857481383}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, booktitle = {IABSE Conference, Nara 2015: Elegance in Structures - Report}, pages = {48--49}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {"The walls between art and engineering exist only in our minds." (Theo Jansen). Structural Engineering is a combination of Science and Art. Science is based in universal laws and is valid for everyone and for all times. Art and Aesthetic are more personal and changeable with culture and time. Elegance from the point of view of engineering could be formulated as the right combination of several factors such as: scale, blending with the context, functionality, efficiency, detailing, influence in the public realm, and a sense of timeless. The proper addressing to the aforementioned factors is vital in the aesthetical result of the structure. In the paper, a discussion of the conceptual design and the influence of those variables in the outcome are being presented.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } "The walls between art and engineering exist only in our minds." (Theo Jansen). Structural Engineering is a combination of Science and Art. Science is based in universal laws and is valid for everyone and for all times. Art and Aesthetic are more personal and changeable with culture and time. Elegance from the point of view of engineering could be formulated as the right combination of several factors such as: scale, blending with the context, functionality, efficiency, detailing, influence in the public realm, and a sense of timeless. The proper addressing to the aforementioned factors is vital in the aesthetical result of the structure. In the paper, a discussion of the conceptual design and the influence of those variables in the outcome are being presented. |
Romo, J; Bögle, A; Meyboom, A Geometry and parametric modeling in the conceptual design of bridges Conference IABSE Conference, Geneva 2015: Structural Engineering: Providing Solutions to Global Challenges - Report, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2015, ISBN: 9783857481406. @conference{Romo2015433, title = {Geometry and parametric modeling in the conceptual design of bridges}, author = {J Romo and A Bögle and A Meyboom}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84971265075&partnerID=40&md5=e360853381d49a9e9c03809dc920a89d}, isbn = {9783857481406}, year = {2015}, date = {2015-01-01}, booktitle = {IABSE Conference, Geneva 2015: Structural Engineering: Providing Solutions to Global Challenges - Report}, pages = {433--442}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {Parametric techniques are developing as an agile tool in both civil engineering and architectural design. What is especially powerful is the ability of these softwares to relate and iterate through multiple options with minimal effort. The tools that combine a parametric definition of the bridge with a 3D graphic and a FEM model gives the designer the opportunity to analyse instantaneously, the effect in the variation of the variable parameters in terms of visual appearance as well as structural behaviour simultaneously. Therefore parametric design is a valuable tool in the conceptual design phase where the geometric decisions made are the most structurally and architecturally impactful.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } Parametric techniques are developing as an agile tool in both civil engineering and architectural design. What is especially powerful is the ability of these softwares to relate and iterate through multiple options with minimal effort. The tools that combine a parametric definition of the bridge with a 3D graphic and a FEM model gives the designer the opportunity to analyse instantaneously, the effect in the variation of the variable parameters in terms of visual appearance as well as structural behaviour simultaneously. Therefore parametric design is a valuable tool in the conceptual design phase where the geometric decisions made are the most structurally and architecturally impactful. |
2014 |
Turrini, N; Pérez Caldentey, A; Mazzarolo, E; Briseghella, B; Cano, L A discrete bond law for precast panels systems without reinforcement Inproceedings Engineering for Progress, Nature and People, pp. 1149–1156, 2014, ISBN: 9783857481352. @inproceedings{Turrini2014a, title = {A discrete bond law for precast panels systems without reinforcement}, author = {N Turrini and A {Pérez Caldentey} and E Mazzarolo and B Briseghella and L Cano}, isbn = {9783857481352}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, booktitle = {Engineering for Progress, Nature and People}, pages = {1149--1156}, abstract = {This paper discusses the possible application of finite element non-linear modelling to a construction system using precast concrete panels. Details are given of the shell elements used for modelling panels and joints, focusing in detail on the non-linear law conferred to the link elements used to represent resistance to relative sliding movement at the interface among panels. The paper relates in particular to an emulative system using cast-in-place joints, without transverse reinforcement. Also the results of pushover analyses, conducted first on a single wall (with the purpose of studying the effect of joint failure on the capacity of the system), then on an entire building erected using the same construction system are presented, assessing the applicability in seismic regions and considering different numbers of storeys.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } This paper discusses the possible application of finite element non-linear modelling to a construction system using precast concrete panels. Details are given of the shell elements used for modelling panels and joints, focusing in detail on the non-linear law conferred to the link elements used to represent resistance to relative sliding movement at the interface among panels. The paper relates in particular to an emulative system using cast-in-place joints, without transverse reinforcement. Also the results of pushover analyses, conducted first on a single wall (with the purpose of studying the effect of joint failure on the capacity of the system), then on an entire building erected using the same construction system are presented, assessing the applicability in seismic regions and considering different numbers of storeys. |
Peiretti, Hugo Corres; García-Arango, Ignacio; Caldentey, Alejandro Pérez; Ramos, Óscar Ramón; Aguilar, Óscar Domínguez; González, Luis Peset Ampliación del puente de Los Santos en la A-8 de 12,00 a 24,60 metros, sin cortes de tráfico Journal Article Hormigón y Acero, 2014. @article{Peiretti2014, title = {Ampliación del puente de Los Santos en la A-8 de 12,00 a 24,60 metros, sin cortes de tráfico}, author = {Hugo Corres Peiretti and Ignacio García-Arango and Alejandro Pérez Caldentey and Óscar Ramón Ramos and Óscar Domínguez Aguilar and Luis Peset González}, doi = {10.1016/j.hya.2014.07.001}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Hormigón y Acero}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Todisco, Leonardo An integrated approach to conceptual design of arch bridges with curved deck Book Technical University of Madrid, Madrid, 2014. @book{Todisco2014, title = {An integrated approach to conceptual design of arch bridges with curved deck}, author = {Leonardo Todisco}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, volume = {Master Tes}, publisher = {Technical University of Madrid}, address = {Madrid}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {book} } |
Corres, H; Soriano, J; Palerm, B; Romero, E Arena Corinthians, the great stadium of the World Cup in Brazil | Arena Corinthians, el gran estadio del Mundial de Brasil Journal Article Revista de Obras Publicas, 161 (3558), pp. 41–50, 2014. @article{Corres2014, title = {Arena Corinthians, the great stadium of the World Cup in Brazil | Arena Corinthians, el gran estadio del Mundial de Brasil}, author = {H Corres and J Soriano and B Palerm and E Romero}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Revista de Obras Publicas}, volume = {161}, number = {3558}, pages = {41--50}, abstract = {The new Arena Corinthians hosted the opening match of the 2014 World Cup. This stadium has long been the dream of the Sports Club Corinthians Paulista and its construction was finally made possible as a result of the Brazil Word Cup. The ground has a permanent capacity of 48,000 spectators which was extended to 68,000 over the World Cup. Work on the stadium began in May 2011 and the design and construction were carried out simultaneously and in record time. The prefabricated structure of the Arena is composed of over 20,000 components, some of which being already prefabricated while other larger elements were built at a plant on site.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The new Arena Corinthians hosted the opening match of the 2014 World Cup. This stadium has long been the dream of the Sports Club Corinthians Paulista and its construction was finally made possible as a result of the Brazil Word Cup. The ground has a permanent capacity of 48,000 spectators which was extended to 68,000 over the World Cup. Work on the stadium began in May 2011 and the design and construction were carried out simultaneously and in record time. The prefabricated structure of the Arena is composed of over 20,000 components, some of which being already prefabricated while other larger elements were built at a plant on site. |
Rodríguez, Pilar Crespo; Alcaide, Alvaro Parrilla; Gepp, José Estaire; Cornejo, Miguel Ortega; Caldentey, Alejandro Pérez Bases de cálculo del Eurocódigo 7. Un cambio en la metodología para el proyecto de cimentaciones Journal Article Hormigón y Acero, 2014. @article{Rodriguez2014, title = {Bases de cálculo del Eurocódigo 7. Un cambio en la metodología para el proyecto de cimentaciones}, author = {Pilar Crespo Rodríguez and Alvaro Parrilla Alcaide and José Estaire Gepp and Miguel Ortega Cornejo and Alejandro Pérez Caldentey}, doi = {10.1016/s0439-5689(14)50005-8}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Hormigón y Acero}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Groli, G; Pérez Caldentey, A; Soto, A G Cracking performance of SCC reinforced with recycled fibres - An experimental study Journal Article Structural Concrete, 15 (2), pp. 136–153, 2014. @article{Groli2014, title = {Cracking performance of SCC reinforced with recycled fibres - An experimental study}, author = {G Groli and A {Pérez Caldentey} and A G Soto}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201300008}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {15}, number = {2}, pages = {136--153}, abstract = {This paper presents an experimental campaign aiming to assess the cracking behaviour of flexural members made with self-compacting concrete (SCC) and reinforced with both rebars and steel fibres recycled from end-of-life tyres (ELT). The characteristics, constructability and performance of this new type of fibre are first discussed. The results of the tests carried out are then presented and discussed. The parameters that have been investigated are: $phi$/$rho$ s,ef , concrete cover and fibre content. The results obtained show improvement in cracking behaviour, especially for low reinforcement ratios and large covers. Results are compared with the predictions of the recently published fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010. The main objective of this investigation is to evaluate the efficiency of a new type of fibre technology for crack width control of RC elements, with advantages in sustainability from the point of view of recycling and durability. Copyright textcopyright 2014 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } This paper presents an experimental campaign aiming to assess the cracking behaviour of flexural members made with self-compacting concrete (SCC) and reinforced with both rebars and steel fibres recycled from end-of-life tyres (ELT). The characteristics, constructability and performance of this new type of fibre are first discussed. The results of the tests carried out are then presented and discussed. The parameters that have been investigated are: $phi$/$rho$ s,ef , concrete cover and fibre content. The results obtained show improvement in cracking behaviour, especially for low reinforcement ratios and large covers. Results are compared with the predictions of the recently published fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010. The main objective of this investigation is to evaluate the efficiency of a new type of fibre technology for crack width control of RC elements, with advantages in sustainability from the point of view of recycling and durability. Copyright textcopyright 2014 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin. |
Reineck, K -H; Todisco, L Database of shear tests for non-slender reinforced concrete beams without stirrups Journal Article ACI Structural Journal, 111 (6), pp. 1363–1371, 2014, ISSN: 08893241. @article{Reineck2014, title = {Database of shear tests for non-slender reinforced concrete beams without stirrups}, author = {K -H Reineck and L Todisco}, issn = {08893241}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {ACI Structural Journal}, volume = {111}, number = {6}, pages = {1363--1371}, abstract = {textcopyright 2014, American Concrete Institute. A database is presented with shear tests on non-slender beams without stirrups subjected to point loads with shear span to effective depth ratios (a/d) textless 2.4. From the 338 collected shear tests, 222 tests remained for the evaluations after several selection criteria were applied. The tests were compared with the left part of the shear valley by Kani and did not confirm the strength increase up to the flexural strength in the range from a/d = 2.4 to approximately 1.0. The test results were compared to the strut-And-tie model according to ACI 318-11. The model overestimated the test results. The reduction factor for the strength of the unreinforced struts should be reduced to ß s = 0.42 instead of 0.60 for a strut without reinforcement, such as the inclined strut transferring the load to the support for a point load near an end support.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2014, American Concrete Institute. A database is presented with shear tests on non-slender beams without stirrups subjected to point loads with shear span to effective depth ratios (a/d) textless 2.4. From the 338 collected shear tests, 222 tests remained for the evaluations after several selection criteria were applied. The tests were compared with the left part of the shear valley by Kani and did not confirm the strength increase up to the flexural strength in the range from a/d = 2.4 to approximately 1.0. The test results were compared to the strut-And-tie model according to ACI 318-11. The model overestimated the test results. The reduction factor for the strength of the unreinforced struts should be reduced to ß s = 0.42 instead of 0.60 for a strut without reinforcement, such as the inclined strut transferring the load to the support for a point load near an end support. |
Peiretti, H C; Parrotta, J E; Oregui, A B; Caldentey, A P; Fernandez, F A Experimental study of thermal actions on a solid slab concrete deck bridge and comparison with eurocode 1 Journal Article Journal of Bridge Engineering, 19 (10), 2014. @article{Peiretti2014b, title = {Experimental study of thermal actions on a solid slab concrete deck bridge and comparison with eurocode 1}, author = {H C Peiretti and J E Parrotta and A B Oregui and A P Caldentey and F A Fernandez}, doi = {10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000614}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Journal of Bridge Engineering}, volume = {19}, number = {10}, abstract = {textcopyright 2014 American Society of Civil Engineers. This paper presents extensive temperature measurements obtained during a period of 4 years in an integral solid slab prestressed concrete bridge deck. There is very little experimental information available for this bridge typology. The quality of the measured temperature data are validated by comparing experimentally measured displacements at the ends of the bridge with theoretical displacements determined with the recorded temperature components. The measured temperatures are also compared with common design parameters made considering the specifications for thermal actions proposed by Eurocode 1. The results corroborate that the Eurocode 1 formulations are generally adequate to represent thermal actions on bridges; however, it may need to be complemented to define maximum and minimum temperatures for bridges in locations with daily temperature variations greater than 10°C.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } textcopyright 2014 American Society of Civil Engineers. This paper presents extensive temperature measurements obtained during a period of 4 years in an integral solid slab prestressed concrete bridge deck. There is very little experimental information available for this bridge typology. The quality of the measured temperature data are validated by comparing experimentally measured displacements at the ends of the bridge with theoretical displacements determined with the recorded temperature components. The measured temperatures are also compared with common design parameters made considering the specifications for thermal actions proposed by Eurocode 1. The results corroborate that the Eurocode 1 formulations are generally adequate to represent thermal actions on bridges; however, it may need to be complemented to define maximum and minimum temperatures for bridges in locations with daily temperature variations greater than 10°C. |
Parrotta, J E; Peiretti, H C; Gribniak, V; Caldentey, A P Investigating deformations of RC beams: Experimental and analytical study Journal Article Computers and Concrete, 13 (6), pp. 799–827, 2014. @article{Parrotta2014a, title = {Investigating deformations of RC beams: Experimental and analytical study}, author = {J E Parrotta and H C Peiretti and V Gribniak and A P Caldentey}, doi = {10.12989/cac.2014.13.6.799}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Computers and Concrete}, volume = {13}, number = {6}, pages = {799--827}, abstract = {In this paper, a theoretical and experimental study of the sectional behaviour of reinforced concrete beams subjected to short-term loads is carried out. The pure bending behaviour is analysed with moment-curvature diagrams. Thus, the experimental results obtained from 24 beams tested by the authors and reported in literature are compared with theoretical results obtained from a layered model, which combines the material parameters defined in Model Code 2010 with some of the most recognized tension-stiffening models. Although the tests were carried out for short-term loads, the analysis demonstrates that rheological effects can be important and must be accounted to understand the experimental results. Another important conclusion for the beams tested in this work is that the method proposed by EC-2 tends to underestimate the tension-stiffening effects, leading to inaccuracies in the estimations of deflections. Thus, the actual formulation is analysed and a simple modification is proposed. The idea is the separation of the deflection prediction in two parts: one for short-term loads and other for rheological effects (shrinkage). The results obtained are in fairly good agreement with the experimental results, showing the feasibility of the proposed modification. Copyright textcopyright 2014 Techno-Press, Ltd.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } In this paper, a theoretical and experimental study of the sectional behaviour of reinforced concrete beams subjected to short-term loads is carried out. The pure bending behaviour is analysed with moment-curvature diagrams. Thus, the experimental results obtained from 24 beams tested by the authors and reported in literature are compared with theoretical results obtained from a layered model, which combines the material parameters defined in Model Code 2010 with some of the most recognized tension-stiffening models. Although the tests were carried out for short-term loads, the analysis demonstrates that rheological effects can be important and must be accounted to understand the experimental results. Another important conclusion for the beams tested in this work is that the method proposed by EC-2 tends to underestimate the tension-stiffening effects, leading to inaccuracies in the estimations of deflections. Thus, the actual formulation is analysed and a simple modification is proposed. The idea is the separation of the deflection prediction in two parts: one for short-term loads and other for rheological effects (shrinkage). The results obtained are in fairly good agreement with the experimental results, showing the feasibility of the proposed modification. Copyright textcopyright 2014 Techno-Press, Ltd. |
PUSHOVER ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES MADE FROM CONCRETE PANELS. VERIFICATION OF SHEAR FAILURE AT THE PANEL JOINTS Inproceedings 2014. @inproceedings{, title = {PUSHOVER ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES MADE FROM CONCRETE PANELS. VERIFICATION OF SHEAR FAILURE AT THE PANEL JOINTS}, doi = {10.13140/2.1.4198.2085}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } |
Groli, G; Pérez Caldentey, A; Giraldo Soto, A; Marchetto, F; Ezeberry Parrotta, J Simplified serviceability design of jointless structures. Experimental verification and application to typical bridge and building structures Journal Article Engineering Structures, 59 , pp. 469–483, 2014. @article{Groli2014b, title = {Simplified serviceability design of jointless structures. Experimental verification and application to typical bridge and building structures}, author = {G Groli and A {Pérez Caldentey} and A {Giraldo Soto} and F Marchetto and J {Ezeberry Parrotta}}, doi = {10.1016/j.engstruct.2013.11.018}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Engineering Structures}, volume = {59}, pages = {469--483}, abstract = {In this article an experimental campaign aimed at validating a previously published simplified serviceability design method of the columns of long jointless structures is presented. The proposed method is also extended to include tension stiffening effects which proved to be significant in structures with small amount of reinforcement subjected to small axial loading. This extension allows significant improvement of predictions for this type of element. The campaign involved columns with different reinforcement and squashing load ratios, given that these parameters had been identified as crucial when designing columns subjected to imposed displacements. Experimental results are presented and discussed, with particular regard to cracking behaviour and structural stiffness. Considerations on tension stiffening effects are also made. Finally, the application of the method to typical bridge and building cases is presented, showing the feasibility of jointless construction, and the limits which should be respected. textcopyright 2013 Elsevier Ltd.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } In this article an experimental campaign aimed at validating a previously published simplified serviceability design method of the columns of long jointless structures is presented. The proposed method is also extended to include tension stiffening effects which proved to be significant in structures with small amount of reinforcement subjected to small axial loading. This extension allows significant improvement of predictions for this type of element. The campaign involved columns with different reinforcement and squashing load ratios, given that these parameters had been identified as crucial when designing columns subjected to imposed displacements. Experimental results are presented and discussed, with particular regard to cracking behaviour and structural stiffness. Considerations on tension stiffening effects are also made. Finally, the application of the method to typical bridge and building cases is presented, showing the feasibility of jointless construction, and the limits which should be respected. textcopyright 2013 Elsevier Ltd. |
Romo, J Exploring structural shapes in steel bridges: Bending constraints Conference Engineering for Progress, Nature and People, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2014, ISBN: 9783857481352. @conference{Romo20141603, title = {Exploring structural shapes in steel bridges: Bending constraints}, author = {J Romo}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84929429160&partnerID=40&md5=6f6e7860a8227926e78df33058a0cf73}, isbn = {9783857481352}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, booktitle = {Engineering for Progress, Nature and People}, pages = {1603--1610}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {During the final decades of the XXth Century and these early years of the XXIst Century, steel structures' design and fabrication techniques, as the CAD-CAM systems, modern welding, and powerful construction systems give the designer a new freedom, making possible almost any dreamt form. In this paper some of the possible fields of innovation in steel bridges are presented.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } During the final decades of the XXth Century and these early years of the XXIst Century, steel structures' design and fabrication techniques, as the CAD-CAM systems, modern welding, and powerful construction systems give the designer a new freedom, making possible almost any dreamt form. In this paper some of the possible fields of innovation in steel bridges are presented. |
Bögle, A; Ortolano, J M; Romo, J Use of Parametric Design techniques applied to Civil Engineering Conference Engineering for Progress, Nature and People, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2014, ISBN: 9783857481352. @conference{Bögle20141587, title = {Use of Parametric Design techniques applied to Civil Engineering}, author = {A Bögle and J M Ortolano and J Romo}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84929448581&partnerID=40&md5=b3890d3afbdd8bab153cfc1496466c2d}, isbn = {9783857481352}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, booktitle = {Engineering for Progress, Nature and People}, pages = {1587--1594}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {Parametric Design has appeared recently for expressing a new paradigm in the field of design. This new methodology has been applied recently in the field of architecture. However, in the case of Civil Engineering, the number of examples that illustrate the use of parametrics is almost nonexistent. This paper describes the main characteristics and the methodology of Parametric Design as a technique to solve the form-finding problem. A study of the main implications of these techniques for solving engineering problems is carried out. Finally, an implementation in a common engineering problem illustrates this new paradigm.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } Parametric Design has appeared recently for expressing a new paradigm in the field of design. This new methodology has been applied recently in the field of architecture. However, in the case of Civil Engineering, the number of examples that illustrate the use of parametrics is almost nonexistent. This paper describes the main characteristics and the methodology of Parametric Design as a technique to solve the form-finding problem. A study of the main implications of these techniques for solving engineering problems is carried out. Finally, an implementation in a common engineering problem illustrates this new paradigm. |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L New courthouse at El Ejido Journal Article Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 24 (1), pp. 68–73, 2014, ISSN: 10168664. @article{Tanner201468, title = {New courthouse at El Ejido}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84894312842&doi=10.2749%2F101686614X13830788506044&partnerID=40&md5=a692ee13254143566156f91834cb0d12}, doi = {10.2749/101686614X13830788506044}, issn = {10168664}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, journal = {Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, volume = {24}, number = {1}, pages = {68--73}, abstract = {The courthouse at El Ejido has a trapezoid floor plan (47 m × 55/26 m) and comprises two distinct volumes that are structurally connected at the basement level and by the footbridges on the upper storeys. A third trapezoid unit featuring a glazed curtain wall facade cantilevers 8 m off the main facade of the front volume. This facade is a structural diaphragm wall, constituted by nine rows of vertical precast concrete members separated by horizontal cast-in-place, self-compacting concrete chords. The location of the courthouse in a seismic area and the small number of horizontal supports for the facade make this wall potentially vulnerable. The high risk, in particular, during construction required careful planning based on a detailed analysis of the interaction between the structure and the ancillary resources used to build it. textcopyright 2014 Publishing Technology.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The courthouse at El Ejido has a trapezoid floor plan (47 m × 55/26 m) and comprises two distinct volumes that are structurally connected at the basement level and by the footbridges on the upper storeys. A third trapezoid unit featuring a glazed curtain wall facade cantilevers 8 m off the main facade of the front volume. This facade is a structural diaphragm wall, constituted by nine rows of vertical precast concrete members separated by horizontal cast-in-place, self-compacting concrete chords. The location of the courthouse in a seismic area and the small number of horizontal supports for the facade make this wall potentially vulnerable. The high risk, in particular, during construction required careful planning based on a detailed analysis of the interaction between the structure and the ancillary resources used to build it. textcopyright 2014 Publishing Technology. |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L New courthouse at El Ejido Conference Engineering for Progress, Nature and People, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2014, ISBN: 9783857481352. @conference{Tanner20142295, title = {New courthouse at El Ejido}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84929429084&partnerID=40&md5=e0731457fe3dbd885b62c4ddf84c8b49}, isbn = {9783857481352}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, booktitle = {Engineering for Progress, Nature and People}, pages = {2295--2302}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {The courthouse at El Ejido has a trapezoid floor plan (47 m x 55/26 m) and comprises two distinct volumes that are structurally connected at basement level and by footbridges on the upper storeys. A third trapezoid unit featuring a glazed curtain wall façade cantilevers 8 m off the main façade of the front volume. This façade is a structural diaphragm wall, constituted by nine rows of vertical precast concrete members separated by horizontal cast-in-place, self-compacting concrete chords. The location of the courthouse in a seismic area and the short number of horizontal supports for the façade make this wall potentially vulnerable. The particularly high risk during construction called for careful planning based on a detailed analysis of the interaction between the structure and the ancillary resources used to build it.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } The courthouse at El Ejido has a trapezoid floor plan (47 m x 55/26 m) and comprises two distinct volumes that are structurally connected at basement level and by footbridges on the upper storeys. A third trapezoid unit featuring a glazed curtain wall façade cantilevers 8 m off the main façade of the front volume. This façade is a structural diaphragm wall, constituted by nine rows of vertical precast concrete members separated by horizontal cast-in-place, self-compacting concrete chords. The location of the courthouse in a seismic area and the short number of horizontal supports for the façade make this wall potentially vulnerable. The particularly high risk during construction called for careful planning based on a detailed analysis of the interaction between the structure and the ancillary resources used to build it. |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L; Hingorani, R; Sanz, D Learning from incidents during bridge erection Conference Engineering for Progress, Nature and People, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2014, ISBN: 9783857481352. @conference{Tanner20141047, title = {Learning from incidents during bridge erection}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod and R Hingorani and D Sanz}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84929448338&partnerID=40&md5=f42772ea508484c8bc9d8bcc5de9e2fd}, isbn = {9783857481352}, year = {2014}, date = {2014-01-01}, booktitle = {Engineering for Progress, Nature and People}, pages = {1047--1054}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {Bridge building is a highly uncertain endeavour that entails considerable risk, as attested to by the succession of construction-related incidents and accidents recently reported in Spain and elsewhere. While efforts are being made to improve on-site safety, many issues are still outstanding, such as the establishment of reliability requirements for the ancillary systems used. The problems that must be dealt with in everyday practice, however, are more elementary and often attributable to human error. The overall organisation of the use of bridge construction equipment is in need of improvement. Close cooperation between the bridge engineers responsible for construction planning and ancillary element suppliers is imperative, for flawed interaction between building equipment and the bridge under construction may generate structural vulnerability. External quality assurance should likewise be mandatory.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } Bridge building is a highly uncertain endeavour that entails considerable risk, as attested to by the succession of construction-related incidents and accidents recently reported in Spain and elsewhere. While efforts are being made to improve on-site safety, many issues are still outstanding, such as the establishment of reliability requirements for the ancillary systems used. The problems that must be dealt with in everyday practice, however, are more elementary and often attributable to human error. The overall organisation of the use of bridge construction equipment is in need of improvement. Close cooperation between the bridge engineers responsible for construction planning and ancillary element suppliers is imperative, for flawed interaction between building equipment and the bridge under construction may generate structural vulnerability. External quality assurance should likewise be mandatory. |
2013 |
Ramos, A; León, J Classification of backfill at the extrados of masonry vaults | Clasificación morfológica de los rellenos en el trasdós de bóvedas de fábrica Journal Article Informes de la Construccion, 65 (532), pp. 471–480, 2013. @article{Ramos2013, title = {Classification of backfill at the extrados of masonry vaults | Clasificación morfológica de los rellenos en el trasdós de bóvedas de fábrica}, author = {A Ramos and J León}, doi = {10.3989/ic.12.062}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Informes de la Construccion}, volume = {65}, number = {532}, pages = {471--480}, abstract = {This paper proposes a classification of the different type of backfill (granular, stiff or masonry backup) at the extrados of vaults of historical masonry buildings scattered throughout the Iberian Peninsula. This study, in the mainframe of a broader research program, highlights the structural significance, rather disregarded in literature, of the backfill regarding the structural stability of such constructions. Furthermore, the most common patterns of the arrangement of masonry backup and backfill, as well as some structural considerations, are depicted to illustrate how to evaluate their structural contribution.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } This paper proposes a classification of the different type of backfill (granular, stiff or masonry backup) at the extrados of vaults of historical masonry buildings scattered throughout the Iberian Peninsula. This study, in the mainframe of a broader research program, highlights the structural significance, rather disregarded in literature, of the backfill regarding the structural stability of such constructions. Furthermore, the most common patterns of the arrangement of masonry backup and backfill, as well as some structural considerations, are depicted to illustrate how to evaluate their structural contribution. |
Pérez Caldentey, A; Corres Peiretti, H; Giraldo Soto, A; Peset Iribarren, J Structural Concrete, 14 (1), pp. 69–78, 2013. @article{PerezCaldentey2013b, title = {Cracking of RC members revisited: Influence of cover, $phi$/$rho$ textlessinftextgreaters, eftextless/inftextgreater and stirrup spacing - An experimental and theoretical study}, author = {A {Pérez Caldentey} and H {Corres Peiretti} and A {Giraldo Soto} and J {Peset Iribarren}}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201200016}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {14}, number = {1}, pages = {69--78}, abstract = {This article describes an experimental programme aimed at studying the effect of cover, ratio between diameter and effective reinforcement ratio ($phi$/$rho$ s, ef ) and the influence of stirrup spacing on the cracking behaviour of reinforced concrete elements. The experimental programme was conceived in order to contribute to the debate - fuelled by the publication in recent years of Eurocode 2 EN1992-1-1 and the revision of the Model Code under way when the tests were carried out (and now published as a finalized document) - regarding the influence of these parameters on cracking. Important theoretical aspects are discussed, including where the crack width is estimated by current code formulations and what relevance this may have on the correlation between crack opening and durability of RC structures, especially with regard to structures with large covers. The effect of stirrup spacing, a variable absent from current codes, is also discussed. Copyright textcopyright 2013 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } This article describes an experimental programme aimed at studying the effect of cover, ratio between diameter and effective reinforcement ratio ($phi$/$rho$ s, ef ) and the influence of stirrup spacing on the cracking behaviour of reinforced concrete elements. The experimental programme was conceived in order to contribute to the debate - fuelled by the publication in recent years of Eurocode 2 EN1992-1-1 and the revision of the Model Code under way when the tests were carried out (and now published as a finalized document) - regarding the influence of these parameters on cracking. Important theoretical aspects are discussed, including where the crack width is estimated by current code formulations and what relevance this may have on the correlation between crack opening and durability of RC structures, especially with regard to structures with large covers. The effect of stirrup spacing, a variable absent from current codes, is also discussed. Copyright textcopyright 2013 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin. |
Balázs, G L; Bisch, P; õ, Borosny A; Burdet, O; Burns, C; Ceroni, F; Cervenka, V; Chiorino, M A; Debernardi, P; Eckfeldt, L; El-Badry, M; Fehling, E; Foster, S J; Ghali, A; Gribniak, V; Guiglia, M; Kaklauskas, G; Lark, R J; Lenkei, P; Lorrain, M; Marí, A; Ozbolt, J; Pecce, M; Pérez Caldentey, A; Taliano, M; Tkalcic, D; Torrenti, J M; Torres, L; Toutlemonde, F; Ueda, T; Vitek, J L; Vráblík, L Design for SLS according to fib Model Code 2010 Journal Article Structural Concrete, 14 (2), pp. 99–123, 2013. @article{Balazs2013a, title = {Design for SLS according to fib Model Code 2010}, author = {G L Balázs and P Bisch and A Borosny{õ}i and O Burdet and C Burns and F Ceroni and V Cervenka and M A Chiorino and P Debernardi and L Eckfeldt and M El-Badry and E Fehling and S J Foster and A Ghali and V Gribniak and M Guiglia and G Kaklauskas and R J Lark and P Lenkei and M Lorrain and A Marí and J Ozbolt and M Pecce and A {Pérez Caldentey} and M Taliano and D Tkalcic and J M Torrenti and L Torres and F Toutlemonde and T Ueda and J L Vitek and L Vráblík}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201200060}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {14}, number = {2}, pages = {99--123}, abstract = {This paper provides an overview of serviceability specifications given by the fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010 (fib MC2010 [1]). First, the reasons behind crack control and deflection control are discussed, then specific design rules are provided. Simple rules as well as detailed models are also presented. Numerical examples are provided in order to assist in the application of the design recommendations for crack control and deflection control (reinforced and prestressed concrete elements). Simple rules mean indirect control of cracking or deflections without calculations. Indirect crack control may include limitation of stresses and selection of maximum bar diameter or maximum bar spacing. Indirect deflection control normally means limiting the span-to-depth ratio. Detailed models are based on physical and mathematical approaches to cracking and deflections. The design crack width is expressed as the maximum bond transfer length multiplied by the mean strain between cracks. Deflection analysis can be provided by integrating curvatures or by using a simplified or refined method. Vibrations and numerical modelling of cracking are also briefly discussed. textcopyright 2013 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } This paper provides an overview of serviceability specifications given by the fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010 (fib MC2010 [1]). First, the reasons behind crack control and deflection control are discussed, then specific design rules are provided. Simple rules as well as detailed models are also presented. Numerical examples are provided in order to assist in the application of the design recommendations for crack control and deflection control (reinforced and prestressed concrete elements). Simple rules mean indirect control of cracking or deflections without calculations. Indirect crack control may include limitation of stresses and selection of maximum bar diameter or maximum bar spacing. Indirect deflection control normally means limiting the span-to-depth ratio. Detailed models are based on physical and mathematical approaches to cracking and deflections. The design crack width is expressed as the maximum bond transfer length multiplied by the mean strain between cracks. Deflection analysis can be provided by integrating curvatures or by using a simplified or refined method. Vibrations and numerical modelling of cracking are also briefly discussed. textcopyright 2013 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin. |
Caldentey, A P; Padilla, P; Muttoni, A; Ruiz, M F; Chen, S; Miao, L Effect of load distribution and variable depth on shear resistance of slender beams without stirrups. Journal Article ACI Structural Journal, 110 (4), pp. 703, 2013. @article{Caldentey2013b, title = {Effect of load distribution and variable depth on shear resistance of slender beams without stirrups.}, author = {A P Caldentey and P Padilla and A Muttoni and M F Ruiz and S Chen and L Miao}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {ACI Structural Journal}, volume = {110}, number = {4}, pages = {703}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Petschke, T; Corres, H; Ezeberry, J I; Pérez, A; Recupero, A Expanding the classic moment-curvature relation by a new perspective onto its axial strain Journal Article Computers and Concrete, 11 (6), pp. 515–529, 2013. @article{Petschke2013a, title = {Expanding the classic moment-curvature relation by a new perspective onto its axial strain}, author = {T Petschke and H Corres and J I Ezeberry and A Pérez and A Recupero}, doi = {10.12989/cac.2013.11.6.515}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Computers and Concrete}, volume = {11}, number = {6}, pages = {515--529}, abstract = {The moment-curvature relation for simple bending is a well-studied subject and the classical moment-curvature diagram is commonly found in literature. The influence of axial forces has generally been considered as compression onto symmetrically reinforced cross-sections, thus strain at the reference fiber never has been an issue. However, when dealing with integral structures, which are usually statically indeterminate in different degrees, these concepts are not sufficient. Their horizontal elements are often completely restrained, which, under imposed deformations, leads to moderate compressive or tensile axial forces. The authors propose to analyze conventional beam cross-sections with moment-curvature diagrams considering asymmetrically reinforced cross-sections under combined influence of bending and moderate axial force. In addition a new diagram is introduced that expands the common moment-curvature relation onto the strain variation at the reference fiber. A parametric study presented in this article reveals the significant influence of selected cross-section parameters. Copyright textcopyright 2013 Techno-Press, Ltd.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The moment-curvature relation for simple bending is a well-studied subject and the classical moment-curvature diagram is commonly found in literature. The influence of axial forces has generally been considered as compression onto symmetrically reinforced cross-sections, thus strain at the reference fiber never has been an issue. However, when dealing with integral structures, which are usually statically indeterminate in different degrees, these concepts are not sufficient. Their horizontal elements are often completely restrained, which, under imposed deformations, leads to moderate compressive or tensile axial forces. The authors propose to analyze conventional beam cross-sections with moment-curvature diagrams considering asymmetrically reinforced cross-sections under combined influence of bending and moderate axial force. In addition a new diagram is introduced that expands the common moment-curvature relation onto the strain variation at the reference fiber. A parametric study presented in this article reveals the significant influence of selected cross-section parameters. Copyright textcopyright 2013 Techno-Press, Ltd. |
Peiretti, H C; Caldentey, A P; Femández, F A High speed railroad bridges. Conception, bases of design, typological possibilities and construction methods Inproceedings fib Symposium TEL-AVIV 2013: Engineering a Concrete Future: Technology, Modeling and Construction, Proceedings, pp. 185–188, 2013, ISBN: 9789659203901. @inproceedings{Peiretti2013, title = {High speed railroad bridges. Conception, bases of design, typological possibilities and construction methods}, author = {H C Peiretti and A P Caldentey and F A Femández}, isbn = {9789659203901}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, booktitle = {fib Symposium TEL-AVIV 2013: Engineering a Concrete Future: Technology, Modeling and Construction, Proceedings}, pages = {185--188}, abstract = {Railroad bridges, in general, and those for high speed railways, in particular, demand very special conditions. The traffic loads are much higher than for road bridges. Loads due to braking and acceleration determine, due to their magnitude, the structural layout. Because of the speed of the vehicles there are specific dynamic effects which need to be considered. In order to ensure passenger comfort, compatible with speeds of up to 350 km/h, it is necessary to meet very demanding conditions with respect to stiffness, displacements and dynamic behavior. In this paper these conditions are briefly described and different typological possibilities to satisfy them are presented as well as the main construction methods applicable to this kind of bridges.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } Railroad bridges, in general, and those for high speed railways, in particular, demand very special conditions. The traffic loads are much higher than for road bridges. Loads due to braking and acceleration determine, due to their magnitude, the structural layout. Because of the speed of the vehicles there are specific dynamic effects which need to be considered. In order to ensure passenger comfort, compatible with speeds of up to 350 km/h, it is necessary to meet very demanding conditions with respect to stiffness, displacements and dynamic behavior. In this paper these conditions are briefly described and different typological possibilities to satisfy them are presented as well as the main construction methods applicable to this kind of bridges. |
Petschke, T; García, E; Pérez, A; Corres, H Imposed deformations measured on a real integral structure: New Airport Terminal Barajas, Madrid, Spain Journal Article Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 27 (5), pp. 508–518, 2013. @article{Petschke2013b, title = {Imposed deformations measured on a real integral structure: New Airport Terminal Barajas, Madrid, Spain}, author = {T Petschke and E García and A Pérez and H Corres}, doi = {10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0000351}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities}, volume = {27}, number = {5}, pages = {508--518}, abstract = {Experimental research on imposed deformation is generally conducted on small-scale laboratory experiments. The attractiveness of field research lies in the possibility to compare results obtained from full-scale structures to theoretical predictions. Unfortunately, measurements obtained from real structures are rarely described in literature. The structural response of integral edifices depends significantly on stiffness changes and constraints. The New Airport Terminal Barajas in Madrid, Spain provides investigators with large integral modules, partially post-tensioned concrete frames, cast monolithically over three floor levels with an overall length of approximately 80 m. The field campaign described in this article explains the instrumentation of one of these frames, focusing on the influence of imposed deformations such as creep, shrinkage, and temperature. The applied monitoring equipment included embedded strain gauges, thermocouples, hand-held mechanical strain gauge measurements, and simple displacement measurements. Data were collected throughout construction and during two years of service. A complete data range of five years is presented and analyzed. Using a simple approach, the results are compared to predict the long-term shortening of this concrete structure. Both analytical and experimental results are discussed. textcopyright 2013 American Society of Civil Engineers.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Experimental research on imposed deformation is generally conducted on small-scale laboratory experiments. The attractiveness of field research lies in the possibility to compare results obtained from full-scale structures to theoretical predictions. Unfortunately, measurements obtained from real structures are rarely described in literature. The structural response of integral edifices depends significantly on stiffness changes and constraints. The New Airport Terminal Barajas in Madrid, Spain provides investigators with large integral modules, partially post-tensioned concrete frames, cast monolithically over three floor levels with an overall length of approximately 80 m. The field campaign described in this article explains the instrumentation of one of these frames, focusing on the influence of imposed deformations such as creep, shrinkage, and temperature. The applied monitoring equipment included embedded strain gauges, thermocouples, hand-held mechanical strain gauge measurements, and simple displacement measurements. Data were collected throughout construction and during two years of service. A complete data range of five years is presented and analyzed. Using a simple approach, the results are compared to predict the long-term shortening of this concrete structure. Both analytical and experimental results are discussed. textcopyright 2013 American Society of Civil Engineers. |
Pérez Caldentey, A; Padilla Lavaselli, P; Corres Peiretti, H; ñ}ez Fernández, {Ari F Influence of stirrup detailing on punching shear strength of flat slabs Journal Article Engineering Structures, 49 , pp. 855–865, 2013. @article{PerezCaldentey2013b, title = {Influence of stirrup detailing on punching shear strength of flat slabs}, author = {A {Pérez Caldentey} and P {Padilla Lavaselli} and H {Corres Peiretti} and F {Ari{ñ}ez Fernández}}, doi = {10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.12.032}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Engineering Structures}, volume = {49}, pages = {855--865}, abstract = {Most concrete design codes agree that it is important for punching shear reinforcement stirrups in slabs to engage the tensile longitudinal reinforcement bars. However, due to the practical difficulties that this anchorage detail entails, it has been common construction practice in some countries (including Spain) to place closed stirrups without encircling the main tensile reinforcement. The Structural Concrete Research Group at the Polytechnic University of Madrid tested eight slabs with four different shear reinforcement dispositions and the results show that slabs with the shear reinforcement disposition that matches Spanish practice show punching shear strength that is quite similar to the one shown by slabs with the transverse reinforcement disposition specified in the codes. The results also show a significant reduction in punching shear strength when longitudinal reinforcement does not pass through the slab-column connection. textcopyright 2013 Elsevier Ltd.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Most concrete design codes agree that it is important for punching shear reinforcement stirrups in slabs to engage the tensile longitudinal reinforcement bars. However, due to the practical difficulties that this anchorage detail entails, it has been common construction practice in some countries (including Spain) to place closed stirrups without encircling the main tensile reinforcement. The Structural Concrete Research Group at the Polytechnic University of Madrid tested eight slabs with four different shear reinforcement dispositions and the results show that slabs with the shear reinforcement disposition that matches Spanish practice show punching shear strength that is quite similar to the one shown by slabs with the transverse reinforcement disposition specified in the codes. The results also show a significant reduction in punching shear strength when longitudinal reinforcement does not pass through the slab-column connection. textcopyright 2013 Elsevier Ltd. |
Pérez Caldentey, A; Marchetto, F; Corres Peiretti, H; Iglesias Villareal, J Plate-anchored reinforcement bars: A new simple and physical model for practical applications Journal Article Engineering Structures, 52 , pp. 168–178, 2013. @article{PerezCaldentey2013h, title = {Plate-anchored reinforcement bars: A new simple and physical model for practical applications}, author = {A {Pérez Caldentey} and F Marchetto and H {Corres Peiretti} and J {Iglesias Villareal}}, doi = {10.1016/j.engstruct.2013.02.019}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Engineering Structures}, volume = {52}, pages = {168--178}, abstract = {A new model, based on sound simple physical considerations, allowing the assessment of the capacity of concrete to carry concentrated loads without transverse reinforcement is presented with a view for its application to the practical case of plate anchored reinforcement bars. The model is compared to experimental evidence and to other existing models obtaining excellent agreement with tests and improved performance with respect to existing models. Finally, the safety of the proposed model is also considered by applying the standard Eurocode format. With this format the resulting safety level is shown to be adequate. It is also shown that an equivalent safety level can be achieved using the traditional North American safety format (as in ACI-318, for instance).The proposed formulation is easy to use and allows the consideration of all relevant data in the design of anchor plates for specific conditions (materials, geometry). textcopyright 2013 Elsevier Ltd.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } A new model, based on sound simple physical considerations, allowing the assessment of the capacity of concrete to carry concentrated loads without transverse reinforcement is presented with a view for its application to the practical case of plate anchored reinforcement bars. The model is compared to experimental evidence and to other existing models obtaining excellent agreement with tests and improved performance with respect to existing models. Finally, the safety of the proposed model is also considered by applying the standard Eurocode format. With this format the resulting safety level is shown to be adequate. It is also shown that an equivalent safety level can be achieved using the traditional North American safety format (as in ACI-318, for instance).The proposed formulation is easy to use and allows the consideration of all relevant data in the design of anchor plates for specific conditions (materials, geometry). textcopyright 2013 Elsevier Ltd. |
Corres-Peiretti, H Sound engineering through conceptual design according to the fib Model Code 2010 Journal Article Structural Concrete, 14 (2), pp. 89–98, 2013. @article{Corres-Peiretti2013, title = {Sound engineering through conceptual design according to the fib Model Code 2010}, author = {H Corres-Peiretti}, doi = {10.1002/suco.201200042}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {14}, number = {2}, pages = {89--98}, abstract = {Conceptual design is the approach that creates an idea in order to find a solution to a new proposal for a structure or solve a detail in a specific structure. It is a personal approach that is learned over time and with experience. It is not normally dealt with at university, but is vitally important for producing sound structures. The fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010 introduced this concept in the first section of chapter 7 "Design". The content of that section explains the general approach to developing conceptual design. This paper will show different examples of conceptual design following the general guidelines stated in the Model Code. textcopyright 2013 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Conceptual design is the approach that creates an idea in order to find a solution to a new proposal for a structure or solve a detail in a specific structure. It is a personal approach that is learned over time and with experience. It is not normally dealt with at university, but is vitally important for producing sound structures. The fib Model Code for Concrete Structures 2010 introduced this concept in the first section of chapter 7 "Design". The content of that section explains the general approach to developing conceptual design. This paper will show different examples of conceptual design following the general guidelines stated in the Model Code. textcopyright 2013 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin. |
Corres, H; Defant, M F; Caldentey, A P; Femández, F A Typological, placement possibilities and limitations of ductile behavior of bridges in seismic areas Inproceedings fib Symposium TEL-AVIV 2013: Engineering a Concrete Future: Technology, Modeling and Construction, Proceedings, pp. 565–568, 2013, ISBN: 9789659203901. @inproceedings{Corres2013a, title = {Typological, placement possibilities and limitations of ductile behavior of bridges in seismic areas}, author = {H Corres and M F Defant and A P Caldentey and F A Femández}, isbn = {9789659203901}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, booktitle = {fib Symposium TEL-AVIV 2013: Engineering a Concrete Future: Technology, Modeling and Construction, Proceedings}, pages = {565--568}, abstract = {This paper examines the ductile behaviour of a highway overpass located in a seismic zone. The results of a pushover analysis enabling the independent estimation of the structure's behavior in two directions are presented. The differences with theoretical bilinear behavior are described and explained. Indications are given on the need and possibilities of taking advantage of ductility in different seismic events scenarios.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } This paper examines the ductile behaviour of a highway overpass located in a seismic zone. The results of a pushover analysis enabling the independent estimation of the structure's behavior in two directions are presented. The differences with theoretical bilinear behavior are described and explained. Indications are given on the need and possibilities of taking advantage of ductility in different seismic events scenarios. |
Romo, J Orio Bridge: An innovative hybrid: Cable stayed - Suspended structure Conference Long Span Bridges and Roofs - Development, Design and Implementation, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2013, ISBN: 9783857481284. @conference{Romo2013, title = {Orio Bridge: An innovative hybrid: Cable stayed - Suspended structure}, author = {J Romo}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84929380341&partnerID=40&md5=554ec8468f4370fa5c50a0e008d9ee94}, isbn = {9783857481284}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, booktitle = {Long Span Bridges and Roofs - Development, Design and Implementation}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {The Orio Bridge is an innovative cable supported bridge of 180 m of main span, with 2 lateral short spans of 65 m each. The cable system is a combination of, a main central suspension cable formed by full locked coil ropes, and a system of stays to support the deck in the area closer to the towers. The cable system is located only in the center axis of the bridge in order to get a more attractive aspect, and is supported by two central masts. The design allows the construction of the main span without temporary supports, even though the cable system is anchored to the deck to avoid the transmission of the horizontal forces of the cables to the ground.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } The Orio Bridge is an innovative cable supported bridge of 180 m of main span, with 2 lateral short spans of 65 m each. The cable system is a combination of, a main central suspension cable formed by full locked coil ropes, and a system of stays to support the deck in the area closer to the towers. The cable system is located only in the center axis of the bridge in order to get a more attractive aspect, and is supported by two central masts. The design allows the construction of the main span without temporary supports, even though the cable system is anchored to the deck to avoid the transmission of the horizontal forces of the cables to the ground. |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L; Sanz, D; Hingorani, R Lessons from incidents attributable to the uncertainties in bridge launching illustrated by a case study Journal Article Civil Engineering and Environmental Systems, 30 (2), pp. 146–161, 2013, ISSN: 10286608. @article{Tanner2013146, title = {Lessons from incidents attributable to the uncertainties in bridge launching illustrated by a case study}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod and D Sanz and R Hingorani}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84877354005&doi=10.1080%2F10286608.2012.733376&partnerID=40&md5=2356ceabc5b90641e6dbb2f441c45784}, doi = {10.1080/10286608.2012.733376}, issn = {10286608}, year = {2013}, date = {2013-01-01}, journal = {Civil Engineering and Environmental Systems}, volume = {30}, number = {2}, pages = {146--161}, abstract = {Like other competitive bridge erection techniques, incremental launching is a highly vulnerable process that entails considerable risks to persons. In steel and composite bridges, in particular, patch loading and other mechanisms that induce instability must be avoided. Considerable uncertainties are associated with both resistances and support reactions during launch operations due to the broad range of factors involved. Nonlinear finite element (FE) analysis is very useful for the explicit verification of both local and overall system stability during steel structure launching. Monitoring, in turn, may be a very powerful tool for reducing the risks associated with such operations. Further research is needed both to establish safety levels for temporary structures and on-site activities and to develop a suitable design format for nonlinear FE analysis. However, in everyday practice, engineers and builders must deal with much more basic problems, often related to the interaction between the structure under construction and the ancillary resources used, as exemplified in the case study described in this contribution. The lessons learnt from such incidents are extremely useful for improving the strategies presently in place to reduce construction-related risks. textcopyright 2013 Copyright Taylor and Francis Group, LLC.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Like other competitive bridge erection techniques, incremental launching is a highly vulnerable process that entails considerable risks to persons. In steel and composite bridges, in particular, patch loading and other mechanisms that induce instability must be avoided. Considerable uncertainties are associated with both resistances and support reactions during launch operations due to the broad range of factors involved. Nonlinear finite element (FE) analysis is very useful for the explicit verification of both local and overall system stability during steel structure launching. Monitoring, in turn, may be a very powerful tool for reducing the risks associated with such operations. Further research is needed both to establish safety levels for temporary structures and on-site activities and to develop a suitable design format for nonlinear FE analysis. However, in everyday practice, engineers and builders must deal with much more basic problems, often related to the interaction between the structure under construction and the ancillary resources used, as exemplified in the case study described in this contribution. The lessons learnt from such incidents are extremely useful for improving the strategies presently in place to reduce construction-related risks. textcopyright 2013 Copyright Taylor and Francis Group, LLC. |
2012 |
Caldentey, A P; Padilla, P; Muttoni, A; Ruiz, M F Effect of load distribution and variable depth on shear resistance of slender beams without stirrups Journal Article ACI Structural Journal, 109 (5), pp. 595–603, 2012. @article{Caldentey2012, title = {Effect of load distribution and variable depth on shear resistance of slender beams without stirrups}, author = {A P Caldentey and P Padilla and A Muttoni and M F Ruiz}, year = {2012}, date = {2012-01-01}, journal = {ACI Structural Journal}, volume = {109}, number = {5}, pages = {595--603}, abstract = {The shear resistance of elements without stirrups has mainly been investigated by test setups involving simply supported beams of constant thickness subjected to one- or two-point loading, and most of the formulas included in codes have been adjusted using this experimental background. It is a fact, however, that most design situations involve constant or triangular distributed loading (such as retaining walls or footings) on tapered members. Furthermore, there seems to be few shear tests involving cantilever structures subjected to distributed loading. These structures, which are common in everyday practice, fail in shear near the clamped end, where the shear forces and bending moments are maximum (contrary to simply supported beams of tests, where shear failures under distributed loading develop near the support region for large shear forces but limited bending moments). In this paper, a specific testing program undertaken at the Polytechnic University of Madrid (UPM), Madrid, Spain, in close collaboration with Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland, is presented. It was aimed at investigating the influence of load distribution and tapered beam geometrics on the shear strength. The experimental program consists of eight slender beams without stirrups. Four specimens had a constant depth, whereas the others had variable depths (maximum depth of 600 mm [23.6 in.]). Each specimen was tested twice: one side was tested first under point loading, and then (after repairing) the other side was tested under either uniform loading or triangular loading. The setup allowed direct comparisons between point and distributed loading. The experimental results showed a significant influence of the type of loading and of tapered geometries on the shear strength. On the basis of these results, and using the fundamentals of the critical shear crack theory, a consistent physical explanation of the observed failure modes and differences in shear strength is provided. Also, comparisons to current design provisions (ACI318-08 and EC2) are discussed. textcopyright 2012, American Concrete Institute.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The shear resistance of elements without stirrups has mainly been investigated by test setups involving simply supported beams of constant thickness subjected to one- or two-point loading, and most of the formulas included in codes have been adjusted using this experimental background. It is a fact, however, that most design situations involve constant or triangular distributed loading (such as retaining walls or footings) on tapered members. Furthermore, there seems to be few shear tests involving cantilever structures subjected to distributed loading. These structures, which are common in everyday practice, fail in shear near the clamped end, where the shear forces and bending moments are maximum (contrary to simply supported beams of tests, where shear failures under distributed loading develop near the support region for large shear forces but limited bending moments). In this paper, a specific testing program undertaken at the Polytechnic University of Madrid (UPM), Madrid, Spain, in close collaboration with Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland, is presented. It was aimed at investigating the influence of load distribution and tapered beam geometrics on the shear strength. The experimental program consists of eight slender beams without stirrups. Four specimens had a constant depth, whereas the others had variable depths (maximum depth of 600 mm [23.6 in.]). Each specimen was tested twice: one side was tested first under point loading, and then (after repairing) the other side was tested under either uniform loading or triangular loading. The setup allowed direct comparisons between point and distributed loading. The experimental results showed a significant influence of the type of loading and of tapered geometries on the shear strength. On the basis of these results, and using the fundamentals of the critical shear crack theory, a consistent physical explanation of the observed failure modes and differences in shear strength is provided. Also, comparisons to current design provisions (ACI318-08 and EC2) are discussed. textcopyright 2012, American Concrete Institute. |
Tobias, P; Hugo, C; Eduardo, G; Alejandro, P Imposed deformations in concrete: Case study of an underground car park Journal Article Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 24 (12), pp. 1513–1519, 2012. @article{Tobias2012a, title = {Imposed deformations in concrete: Case study of an underground car park}, author = {P Tobias and C Hugo and G Eduardo and P Alejandro}, doi = {10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000542}, year = {2012}, date = {2012-01-01}, journal = {Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering}, volume = {24}, number = {12}, pages = {1513--1519}, abstract = {The displacements produced by imposed deformations in buildings are usually compensated for with expansion joints. A field study was conducted in an underground parking facility with large jointless modules to measure the effects of shrinkage and temperature. The advantage of on-site measurements is the possibility to capture the combined effects of different imposed deformations that are usually studied individually in laboratory experiments. This article describes the instrumentation and monitoring procedures, displays and analyzes the registered data, and discusses the obtained results. Ambient and structural temperatures as well as displacements were recorded. Measuring commenced during the initial construction phase and was maintained throughout a period of five years. The measured longitudinal displacements were exclusively caused by shrinkage and temperature, and these displacements were not hindered by structural monolithicity. textcopyright 2012 American Society of Civil Engineers.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The displacements produced by imposed deformations in buildings are usually compensated for with expansion joints. A field study was conducted in an underground parking facility with large jointless modules to measure the effects of shrinkage and temperature. The advantage of on-site measurements is the possibility to capture the combined effects of different imposed deformations that are usually studied individually in laboratory experiments. This article describes the instrumentation and monitoring procedures, displays and analyzes the registered data, and discusses the obtained results. Ambient and structural temperatures as well as displacements were recorded. Measuring commenced during the initial construction phase and was maintained throughout a period of five years. The measured longitudinal displacements were exclusively caused by shrinkage and temperature, and these displacements were not hindered by structural monolithicity. textcopyright 2012 American Society of Civil Engineers. |
Corres, H; Romo, J Keynotes on bridges in Spain since the mid-1980's Journal Article Bautechnik, 89 (2), pp. 111–118, 2012. @article{Corres2012, title = {Keynotes on bridges in Spain since the mid-1980's}, author = {H Corres and J Romo}, doi = {10.1002/bate.201201541}, year = {2012}, date = {2012-01-01}, journal = {Bautechnik}, volume = {89}, number = {2}, pages = {111--118}, abstract = {Spanish bridge engineering has developed creative and efficient answers to the challenges set by the extraordinary development of road and railway infrastructure during the last 25 years. This process provides continuity to the great tradition of good bridge engineering practice based on the ambition of overcoming such engineering challenges. These efforts also resulted in the exploration of new fields: typology, by generating new ideas to improve structural behavior; construction methods, by using new technologies (many of them perfected for other fields of activity) and by innovations using new specific methods for particular cases; structural materials by exploring the benefits of their new possibilities, deepening in the use of traditional composite steel-concrete structures and starting a very interesting process of using composite materials. Consistent with the old aphorism "learning by doing" the lessons learnt from these daring tasks and experiences will remain in the back of these engineers' minds which will ensure continuity for future developments. At the present and in the near future, Spanish bridge engineering must face new challenges in design and construction in foreign countries, taking advantage of the experience gained during the past 25 years. textcopyright 2012 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Spanish bridge engineering has developed creative and efficient answers to the challenges set by the extraordinary development of road and railway infrastructure during the last 25 years. This process provides continuity to the great tradition of good bridge engineering practice based on the ambition of overcoming such engineering challenges. These efforts also resulted in the exploration of new fields: typology, by generating new ideas to improve structural behavior; construction methods, by using new technologies (many of them perfected for other fields of activity) and by innovations using new specific methods for particular cases; structural materials by exploring the benefits of their new possibilities, deepening in the use of traditional composite steel-concrete structures and starting a very interesting process of using composite materials. Consistent with the old aphorism "learning by doing" the lessons learnt from these daring tasks and experiences will remain in the back of these engineers' minds which will ensure continuity for future developments. At the present and in the near future, Spanish bridge engineering must face new challenges in design and construction in foreign countries, taking advantage of the experience gained during the past 25 years. textcopyright 2012 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin. |
Caldentey, A P; Peiretti, H C; Petschke, T P; Parrota, J E; Soto, A G Serviceability design of columns of long jointless structures Journal Article Engineering Structures, 44 , pp. 359–371, 2012. @article{Caldentey2012c, title = {Serviceability design of columns of long jointless structures}, author = {A P Caldentey and H C Peiretti and T P Petschke and J E Parrota and A G Soto}, doi = {10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.06.007}, year = {2012}, date = {2012-01-01}, journal = {Engineering Structures}, volume = {44}, pages = {359--371}, abstract = {A simplified method for the design or verification of the reinforcement of columns of long jointless structures (usually referred to as . integral structures) for serviceability conditions is proposed. The design of the reinforcement of columns of integral structures is generally conditioned by the serviceability limit state (S.L.S.), and in particular by the control of cracking. The main idea behind the method is to simplify the analysis by reducing the behavior of a complex and large structure to that of an isolated column. The proposed method has been tested by comparing its results to a full non-linear analysis of a 200. m long reinforced concrete frame. The main aim of the method is to promote the design of integral structures whose development is hindered by the difficulties encountered in their analysis in normal engineering practice. textcopyright 2012 Elsevier Ltd.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } A simplified method for the design or verification of the reinforcement of columns of long jointless structures (usually referred to as . integral structures) for serviceability conditions is proposed. The design of the reinforcement of columns of integral structures is generally conditioned by the serviceability limit state (S.L.S.), and in particular by the control of cracking. The main idea behind the method is to simplify the analysis by reducing the behavior of a complex and large structure to that of an isolated column. The proposed method has been tested by comparing its results to a full non-linear analysis of a 200. m long reinforced concrete frame. The main aim of the method is to promote the design of integral structures whose development is hindered by the difficulties encountered in their analysis in normal engineering practice. textcopyright 2012 Elsevier Ltd. |
Groli, G; Caldentey, A P; Gelpí, A Use of recycled steel fibres for crack width control of jointless RC structures Inproceedings fib Symposium 2012: Concrete Structures for Sustainable Community - Proceedings, pp. 189–192, 2012, ISBN: 9789198009811. @inproceedings{Groli2012, title = {Use of recycled steel fibres for crack width control of jointless RC structures}, author = {G Groli and A P Caldentey and A Gelpí}, isbn = {9789198009811}, year = {2012}, date = {2012-01-01}, booktitle = {fib Symposium 2012: Concrete Structures for Sustainable Community - Proceedings}, pages = {189--192}, abstract = {Integral structures are of special interest for sustainable construction, since they require both less materials to be built (smaller forces in ULS for better supported structures, smaller second order effects in supports, no elastomeric bearings, no expansion joints, etc.), and less maintenance during service life. On the other hand, crack width control becomes a major issue for this type of structures. In this paper an ongoing research on crack width control enhancement with recycled steel fibres is presented: their use in low volume contents (0.4 to 1%) in integral structures is meant to bring advantages in sustainability from the point of view of both recycling and durability.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } Integral structures are of special interest for sustainable construction, since they require both less materials to be built (smaller forces in ULS for better supported structures, smaller second order effects in supports, no elastomeric bearings, no expansion joints, etc.), and less maintenance during service life. On the other hand, crack width control becomes a major issue for this type of structures. In this paper an ongoing research on crack width control enhancement with recycled steel fibres is presented: their use in low volume contents (0.4 to 1%) in integral structures is meant to bring advantages in sustainability from the point of view of both recycling and durability. |
2011 |
Caldentey, A P; Peiretti, H C; Iribarren, J P Cracking revisited: Results of an experimental program in view of the new model code proposal, including the effect of stirrups on crack spacing Inproceedings fib Symposium PRAGUE 2011: Concrete Engineering for Excellence and Efficiency, Proceedings, pp. 199–202, 2011, ISBN: 9788087158296. @inproceedings{Caldentey2011, title = {Cracking revisited: Results of an experimental program in view of the new model code proposal, including the effect of stirrups on crack spacing}, author = {A P Caldentey and H C Peiretti and J P Iribarren}, isbn = {9788087158296}, year = {2011}, date = {2011-01-01}, booktitle = {fib Symposium PRAGUE 2011: Concrete Engineering for Excellence and Efficiency, Proceedings}, volume = {1}, pages = {199--202}, abstract = {Within the framework of Task Group 4.1 of fib, discussions have been carried during the period 2007-2010 with a view of making a proposal for the revision of the modelling of crack width for the New Model Code 2010[2]. Some of the topics of discussion have been the influence of cover, not explicitly included in MC90[1] , the effect of curvature - i.e. bending vs. tension and the effect of stirrups. In order to contribute to this discussion an experimental program was carried out at the Polytechnic University of Madrid within the framework of research project IDI-20080937 funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology through the Centre for Technological and Industrial Development (CDTI). These tests were designed specifically to study the effects of cover, $phi$/$rho$ eff ratio, the effect of stirrups and the effect of curvature. It was decided to carry out these tests because it was found to be nearly impossible to draw clear conclusions from the existing experimental work due to Jack of information regarding how and where cracks were measured or due to the changes in more than one parameter from test to test. Some of the relevant results of these tests are presented here.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } Within the framework of Task Group 4.1 of fib, discussions have been carried during the period 2007-2010 with a view of making a proposal for the revision of the modelling of crack width for the New Model Code 2010[2]. Some of the topics of discussion have been the influence of cover, not explicitly included in MC90[1] , the effect of curvature - i.e. bending vs. tension and the effect of stirrups. In order to contribute to this discussion an experimental program was carried out at the Polytechnic University of Madrid within the framework of research project IDI-20080937 funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology through the Centre for Technological and Industrial Development (CDTI). These tests were designed specifically to study the effects of cover, $phi$/$rho$ eff ratio, the effect of stirrups and the effect of curvature. It was decided to carry out these tests because it was found to be nearly impossible to draw clear conclusions from the existing experimental work due to Jack of information regarding how and where cracks were measured or due to the changes in more than one parameter from test to test. Some of the relevant results of these tests are presented here. |
Espeche, A D; León, J Estimation of bond strength envelopes for old-to-new concrete interfaces based on a cylinder splitting test Journal Article Construction and Building Materials, 25 (3), pp. 1222–1235, 2011. @article{Espeche2011, title = {Estimation of bond strength envelopes for old-to-new concrete interfaces based on a cylinder splitting test}, author = {A D Espeche and J León}, doi = {10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.09.032}, year = {2011}, date = {2011-01-01}, journal = {Construction and Building Materials}, volume = {25}, number = {3}, pages = {1222--1235}, abstract = {The number of existing structures under rehabilitation has significantly increased over the past two decades; these structures typically require performance improvements including repair and strengthening. Currently, reinforced concrete is widely used in interventions for the rehabilitation of bridges and buildings. Here, we present a method for the estimation of failure envelopes for old-to-new concrete interfaces based on plasticity theory. The proposed Carol-type failure envelope uses the simple splitting tension test, also known as the Brazilian test. The relevant parameters of the envelope - ft′, the tensile strength, c′, cohesion and $phi$′, the friction angle - are assessed by experimentation, a rational formulation and a bibliographic study, respectively. textcopyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The number of existing structures under rehabilitation has significantly increased over the past two decades; these structures typically require performance improvements including repair and strengthening. Currently, reinforced concrete is widely used in interventions for the rehabilitation of bridges and buildings. Here, we present a method for the estimation of failure envelopes for old-to-new concrete interfaces based on plasticity theory. The proposed Carol-type failure envelope uses the simple splitting tension test, also known as the Brazilian test. The relevant parameters of the envelope - ft′, the tensile strength, c′, cohesion and $phi$′, the friction angle - are assessed by experimentation, a rational formulation and a bibliographic study, respectively. textcopyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. |
Todisco, Leonardo Test Evidence for Applying Strut-and-Tie Models to Deep Beams and D-Regions of Beams Journal Article master's degree thesis, Technical University of Bari, Bari, Italy, Oct, 2011. @article{todisco2011test, title = {Test Evidence for Applying Strut-and-Tie Models to Deep Beams and D-Regions of Beams}, author = {Leonardo Todisco}, year = {2011}, date = {2011-01-01}, journal = {master's degree thesis, Technical University of Bari, Bari, Italy, Oct}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
2010 |
Caldentey, A P; Facchini, A; Manna, F; Dalpont, F Designing for blast loading: Robustness in the face of column collapse in RC structures Inproceedings 3rd International fib Congress and Exhibition, Incorporating the PCI Annual Convention and Bridge Conference: Think Globally, Build Locally, Proceedings, 2010, ISBN: 9780937040904. @inproceedings{Caldentey2010, title = {Designing for blast loading: Robustness in the face of column collapse in RC structures}, author = {A P Caldentey and A Facchini and F Manna and F Dalpont}, isbn = {9780937040904}, year = {2010}, date = {2010-01-01}, booktitle = {3rd International fib Congress and Exhibition, Incorporating the PCI Annual Convention and Bridge Conference: Think Globally, Build Locally, Proceedings}, abstract = {The design against blast loading is becoming a more and more common necessity due to the world-wide wave of terrorist attacks. However these are not the only sources of blast loading. Gas explosions for instance, occur with an unsuspected frequency and it seems necessary to take the idea of designing against blast loading from the exotic place it actually occupies and have it introduced into the normal design procedures. A large step in this direction has already been taken by Eurocode 1, part 7 (EN-1991-1-7) which has introduced on an European level the concepts of robustness, column removal and tie elements in order to face the event of column collapse. However the theory behind Eurocode provisions remains rather obscure due to lack of background information and to the large demands it implies in terms of deformation of concrete structures. In this paper, the development of membrane forces in concrete structures subjected to column loss, is examined by means of an example. Nonlinear finite element calculations are tested against the very simplified concept behind capacity of membrane forces whose basis is pure equilibrium. The comparison between the simplicity of equilibrium and the complexity of nonlinear FEA yields quite good agreement thereby confirming the soundness of the simplified approach included in Eurocode 1, part 7.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } The design against blast loading is becoming a more and more common necessity due to the world-wide wave of terrorist attacks. However these are not the only sources of blast loading. Gas explosions for instance, occur with an unsuspected frequency and it seems necessary to take the idea of designing against blast loading from the exotic place it actually occupies and have it introduced into the normal design procedures. A large step in this direction has already been taken by Eurocode 1, part 7 (EN-1991-1-7) which has introduced on an European level the concepts of robustness, column removal and tie elements in order to face the event of column collapse. However the theory behind Eurocode provisions remains rather obscure due to lack of background information and to the large demands it implies in terms of deformation of concrete structures. In this paper, the development of membrane forces in concrete structures subjected to column loss, is examined by means of an example. Nonlinear finite element calculations are tested against the very simplified concept behind capacity of membrane forces whose basis is pure equilibrium. The comparison between the simplicity of equilibrium and the complexity of nonlinear FEA yields quite good agreement thereby confirming the soundness of the simplified approach included in Eurocode 1, part 7. |
Corres, H; Perez, A; Prochazka, J SLS OF CRACKING ACCORDING TO EC2. JUSTIFICATION OF THE PRESENT RULES AND NEW DEVELOPMENTS Journal Article Design of Concrete Structures Using En 1992-1-1, 2010. @article{Corres2010, title = {SLS OF CRACKING ACCORDING TO EC2. JUSTIFICATION OF THE PRESENT RULES AND NEW DEVELOPMENTS}, author = {H Corres and A Perez and J Prochazka}, url = {http://gateway.webofknowledge.com/gateway/Gateway.cgi?GWVersion=2&SrcAuth=ORCID&SrcApp=OrcidOrg&DestLinkType=FullRecord&DestApp=WOS_CPL&KeyUT=WOS:000324078100030&KeyUID=WOS:000324078100030}, year = {2010}, date = {2010-01-01}, journal = {Design of Concrete Structures Using En 1992-1-1}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Romo, J Riudellots high speed line bridge Conference Large Structures and Infrastructures for Environmentally Constrained and Urbanised Areas, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2010, ISBN: 9783857481222. @conference{Romo2010808, title = {Riudellots high speed line bridge}, author = {J Romo}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84929000201&partnerID=40&md5=e443c64c35cf9be133d59ab8f21578b7}, isbn = {9783857481222}, year = {2010}, date = {2010-01-01}, booktitle = {Large Structures and Infrastructures for Environmentally Constrained and Urbanised Areas}, pages = {808--809}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {Riudellots's Bridge is a railway structure located in Catalonia (Spain). The structure combines stiffness conditions with a sense of lightness, by a truss system with a variable depth. The bridge has an important skew and has a special lateral span to avoid any interference with the comfort of the railway traffic.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } Riudellots's Bridge is a railway structure located in Catalonia (Spain). The structure combines stiffness conditions with a sense of lightness, by a truss system with a variable depth. The bridge has an important skew and has a special lateral span to avoid any interference with the comfort of the railway traffic. |
Romo, J; Lastra, J M Cartagena Auditorium facades: A new structural and sustainable skin system Conference Large Structures and Infrastructures for Environmentally Constrained and Urbanised Areas, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 2010, ISBN: 9783857481222. @conference{Romo2010806, title = {Cartagena Auditorium facades: A new structural and sustainable skin system}, author = {J Romo and J M Lastra}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84929008355&partnerID=40&md5=73f0ca8d6718deda395f0b63d5fab533}, isbn = {9783857481222}, year = {2010}, date = {2010-01-01}, booktitle = {Large Structures and Infrastructures for Environmentally Constrained and Urbanised Areas}, pages = {806--807}, publisher = {International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, abstract = {Cartagena Auditorium (Spain) is a building design inside the principle of sustainability. The building has to large facades in which it has been used for the first time, a flat skin of double layer made in EFTE with a self-resistant cable system. The combination of structural innovation with the rational use of the power resources available is one the main features of this sustainable building.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } Cartagena Auditorium (Spain) is a building design inside the principle of sustainability. The building has to large facades in which it has been used for the first time, a flat skin of double layer made in EFTE with a self-resistant cable system. The combination of structural innovation with the rational use of the power resources available is one the main features of this sustainable building. |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L; Sanz, D Elegance and economy - A new viaduct over the River Llobregat Conference Proceedings of SDSS' Rio 2010: International Colloquium Stability and Ductility of Steel Structures, 1 , 2010, ISBN: 9788528501377. @conference{Tanner2010157, title = {Elegance and economy - A new viaduct over the River Llobregat}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod and D Sanz}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84877340033&partnerID=40&md5=9e4d6be1d3287b3c6a4415b131133be7}, isbn = {9788528501377}, year = {2010}, date = {2010-01-01}, booktitle = {Proceedings of SDSS' Rio 2010: International Colloquium Stability and Ductility of Steel Structures}, volume = {1}, pages = {157--164}, abstract = {The viaduct over the River Llobregat at Puig Reig, Spain, illustrates how demanding conditioning factors can serve as inspiration for a satisfactory solution. The functional design adopted, characterized by the simplicity of its lines, was enhanced by the careful shaping of structural members and good detailing. This example shows that modern, technologically advanced bridge design can be compatible with a solution whose elegance meets even the most exacting aesthetic standards, with no need for inefficient members or adornments, at an affordable additional cost over the least expensive solution. The ideas underlying the conceptual design for the River Llobregat bridge, in particular with respect to the specific boundary conditions involved, are explained in the article, along with the actual layout, remarks about the design of structural details and the verification of structural safety during the incremental launching of the steel structure. textcopyright (2010) by COPPE - Federal University of Rio de Janeiro All rights reserved.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {conference} } The viaduct over the River Llobregat at Puig Reig, Spain, illustrates how demanding conditioning factors can serve as inspiration for a satisfactory solution. The functional design adopted, characterized by the simplicity of its lines, was enhanced by the careful shaping of structural members and good detailing. This example shows that modern, technologically advanced bridge design can be compatible with a solution whose elegance meets even the most exacting aesthetic standards, with no need for inefficient members or adornments, at an affordable additional cost over the least expensive solution. The ideas underlying the conceptual design for the River Llobregat bridge, in particular with respect to the specific boundary conditions involved, are explained in the article, along with the actual layout, remarks about the design of structural details and the verification of structural safety during the incremental launching of the steel structure. textcopyright (2010) by COPPE - Federal University of Rio de Janeiro All rights reserved. |
2009 |
Corres-Peiretti, H Editorial: Conceptual design. The only way to create sound structural concrete solutions Journal Article Structural Concrete, 10 (3), pp. 107–108, 2009. @article{Corres-Peiretti2009, title = {Editorial: Conceptual design. The only way to create sound structural concrete solutions}, author = {H Corres-Peiretti}, doi = {10.1680/stco.2009.10.3.107}, year = {2009}, date = {2009-01-01}, journal = {Structural Concrete}, volume = {10}, number = {3}, pages = {107--108}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L; Sanz, D Footbridge over highway A-2, Guadalajara, Spain Journal Article Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 19 (4), pp. 362–365, 2009, ISSN: 10168664. @article{Tanner2009362, title = {Footbridge over highway A-2, Guadalajara, Spain}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod and D Sanz}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-72549110127&doi=10.2749%2F101686609789847091&partnerID=40&md5=6d75e86fbd53bb6a3a88d30ece6d5745}, doi = {10.2749/101686609789847091}, issn = {10168664}, year = {2009}, date = {2009-01-01}, journal = {Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, volume = {19}, number = {4}, pages = {362--365}, abstract = {Public opinion in many communities is contributing to the growing demand for structures that are more than just utilitarian. Bridges, however, are a product of engineering in no need whatsoever of adornments or inefficient members to enhance their elegance. By means of an example, the paper illustrates that good form follows function design yields economic solutions that meet even the most exacting aesthetic standards, provided that the designer observes a few basic rules about structural form, bridge integration in the landscape, transparency, slenderness and harmony.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Public opinion in many communities is contributing to the growing demand for structures that are more than just utilitarian. Bridges, however, are a product of engineering in no need whatsoever of adornments or inefficient members to enhance their elegance. By means of an example, the paper illustrates that good form follows function design yields economic solutions that meet even the most exacting aesthetic standards, provided that the designer observes a few basic rules about structural form, bridge integration in the landscape, transparency, slenderness and harmony. |
2008 |
Corres, H; Romo, J; Romero, E High Rise Buildings. The challenge of a new field of possibilities for the use of structural concrete Inproceedings Proceedings of the International FIB Symposium 2008 - Tailor Made Concrete Structures: New Solutions for our Society, pp. 182, 2008, ISBN: 9780415475358. @inproceedings{Corres2008, title = {High Rise Buildings. The challenge of a new field of possibilities for the use of structural concrete}, author = {H Corres and J Romo and E Romero}, isbn = {9780415475358}, year = {2008}, date = {2008-01-01}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the International FIB Symposium 2008 - Tailor Made Concrete Structures: New Solutions for our Society}, pages = {182}, abstract = {textcopyright 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London. In this paper, the design and construction of several buildings of moderate height (no more that 250m) are analyzed. In all these projects structural concrete has been used for different elements: floorings, special steel-concrete composite columns using high performance concrete, Shear walls, stiffening floors, etc.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } textcopyright 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London. In this paper, the design and construction of several buildings of moderate height (no more that 250m) are analyzed. In all these projects structural concrete has been used for different elements: floorings, special steel-concrete composite columns using high performance concrete, Shear walls, stiffening floors, etc. |
León, J; Corres-Peiretti, H; Prieto, F Inspection and evaluation of existing structures: A task for brave engineers Inproceedings Life-Cycle Civil Engineering - Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE '08, pp. 355–360, 2008, ISBN: 9780415468572. @inproceedings{Leon2008, title = {Inspection and evaluation of existing structures: A task for brave engineers}, author = {J León and H Corres-Peiretti and F Prieto}, isbn = {9780415468572}, year = {2008}, date = {2008-01-01}, booktitle = {Life-Cycle Civil Engineering - Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE '08}, pages = {355--360}, abstract = {Assessing an existing structure implies its in-depth understanding. In the world of Medicine, full understanding of the patient is based on a well studied clinical history, a visual check, analytical tests and, consequently, a comprehensive diagnosis of the causes of the diseases. There is no reason not to apply a similar modus operandi to existing structures. This paper claims for a better education of young engineers, to enable them to understand an existing structure as a part of a fascinating whole and not merely as a mathematical model. textcopyright 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } Assessing an existing structure implies its in-depth understanding. In the world of Medicine, full understanding of the patient is based on a well studied clinical history, a visual check, analytical tests and, consequently, a comprehensive diagnosis of the causes of the diseases. There is no reason not to apply a similar modus operandi to existing structures. This paper claims for a better education of young engineers, to enable them to understand an existing structure as a part of a fascinating whole and not merely as a mathematical model. textcopyright 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London. |
León, J; Corres-Peiretti, H; Pérez-Fadón, S; Herrero, J E; Rodríguez, F; Prieto, F Lifespan evaluation of 8 bridges of the Indiana Toll Road: A case study Inproceedings Life-Cycle Civil Engineering - Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE '08, pp. 595–600, 2008, ISBN: 9780415468572. @inproceedings{Leon2008a, title = {Lifespan evaluation of 8 bridges of the Indiana Toll Road: A case study}, author = {J León and H Corres-Peiretti and S Pérez-Fadón and J E Herrero and F Rodríguez and F Prieto}, isbn = {9780415468572}, year = {2008}, date = {2008-01-01}, booktitle = {Life-Cycle Civil Engineering - Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE '08}, pages = {595--600}, abstract = {This paper shows the practical experience achieved by evaluating the lifespan of some existing structures under extreme weather conditions, in order to decide on either demolition or repair. The applied methodology shows the feasibility of the approach based on "durability engineering" according to mainframe of current models of degradation. Thus, by using both relatively conventional testing methods and the mentioned available models, it was possible to estimate the remaining lifetime of these structures. Nevertheless, some difficulties appear when applying theory to practice, as pointed out in this paper. textcopyright 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } This paper shows the practical experience achieved by evaluating the lifespan of some existing structures under extreme weather conditions, in order to decide on either demolition or repair. The applied methodology shows the feasibility of the approach based on "durability engineering" according to mainframe of current models of degradation. Thus, by using both relatively conventional testing methods and the mentioned available models, it was possible to estimate the remaining lifetime of these structures. Nevertheless, some difficulties appear when applying theory to practice, as pointed out in this paper. textcopyright 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London. |
Corres Peiretti, H; Pérez Caldentey, A; Romo, J; León González, J; Prieto, F; Sánchez Delgado, J The widening of Los Santos bridge. A case study of a tailor-made structure Inproceedings Proceedings of the International FIB Symposium 2008 - Tailor Made Concrete Structures: New Solutions for our Society, pp. 148, 2008, ISBN: 9780415475358. @inproceedings{CorresPeiretti2008, title = {The widening of Los Santos bridge. A case study of a tailor-made structure}, author = {H {Corres Peiretti} and A {Pérez Caldentey} and J Romo and J {León González} and F Prieto and J {Sánchez Delgado}}, isbn = {9780415475358}, year = {2008}, date = {2008-01-01}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the International FIB Symposium 2008 - Tailor Made Concrete Structures: New Solutions for our Society}, pages = {148}, abstract = {textcopyright 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London. In this paper the main features of the Construction project of the widening of Los Santos Bridge are discussed. The project involves the widening of a major 600 m long bridge with spans of 1 50 meters increasing the width of the deck from 12.00 to 24.00 meters, without recurring to an independent structure. The project is based on the idea of providing minimum strengthening of the existing structure. This approach has allowed very important savings but has also required a challenging design project some aspects of which are discussed in this paper.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } textcopyright 2008 Taylor & Francis Group, London. In this paper the main features of the Construction project of the widening of Los Santos Bridge are discussed. The project involves the widening of a major 600 m long bridge with spans of 1 50 meters increasing the width of the deck from 12.00 to 24.00 meters, without recurring to an independent structure. The project is based on the idea of providing minimum strengthening of the existing structure. This approach has allowed very important savings but has also required a challenging design project some aspects of which are discussed in this paper. |
Caldentey, Pérez A; González, León J; Peiretti, Corres H; Romo, J; Prieto, F; Delgado, Sánchez J The widening of Los Santos bridge. A case study of a tailor-made structure Miscellaneous 2008. @misc{Caldentey2008a, title = {The widening of Los Santos bridge. A case study of a tailor-made structure}, author = {Pérez A Caldentey and León J González and Corres H Peiretti and J Romo and F Prieto and Sánchez J Delgado}, doi = {10.1201/9781439828410.ch106}, year = {2008}, date = {2008-01-01}, booktitle = {Tailor Made Concrete Structures}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {misc} } |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L Alinghi base for the 32nd America's Cup, Valencia, Spain Journal Article Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 18 (2), pp. 192–195, 2008, ISSN: 10168664. @article{Tanner2008192, title = {Alinghi base for the 32nd America's Cup, Valencia, Spain}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-44049108055&doi=10.2749%2F101686608784218851&partnerID=40&md5=13f4a4233d4d8a0b51bea1abd66a82ae}, doi = {10.2749/101686608784218851}, issn = {10168664}, year = {2008}, date = {2008-01-01}, journal = {Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, volume = {18}, number = {2}, pages = {192--195}, abstract = {America's Cup Management (ACM), an independent company announced that Valencia, Spain, would host the 32nd America's Cup (AC). The infrastructure works included, 12 bases that would serve as homes before and during the regattas for the defender, Team Alinghi, and each of the 11 challengers from all over the world. The framework designed for Alinghi base was of steel columns, composite beams and composite slabs. The corridor running from Axis A to B was to be bounded by the slanted glass facade, varying in width from 0,7 m on the ground to 2,9 m on the second storey. The building was to be fitted with a bracing system to transmit the horizontal forces due to wind action. The hollow section steel columns were converted to composite columns in which the concrete infill would stiffen the slender steel constituent plates. A coherent and modern structural approach was adopted that ensured the efficient use of materials.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } America's Cup Management (ACM), an independent company announced that Valencia, Spain, would host the 32nd America's Cup (AC). The infrastructure works included, 12 bases that would serve as homes before and during the regattas for the defender, Team Alinghi, and each of the 11 challengers from all over the world. The framework designed for Alinghi base was of steel columns, composite beams and composite slabs. The corridor running from Axis A to B was to be bounded by the slanted glass facade, varying in width from 0,7 m on the ground to 2,9 m on the second storey. The building was to be fitted with a bracing system to transmit the horizontal forces due to wind action. The hollow section steel columns were converted to composite columns in which the concrete infill would stiffen the slender steel constituent plates. A coherent and modern structural approach was adopted that ensured the efficient use of materials. |
2007 |
Peiretti, H C; Liz, J T; Mateos, J M; Pérez, A R; Martín, J R; Caldentey, A P New bridge over the tajuna river in Spain Inproceedings Concrete Structures - Stimulators of Development, Proceedings of the fib Symposium Dubrovnik 2007, pp. 955–962, 2007, ISBN: 9789539542830. @inproceedings{Peiretti2007, title = {New bridge over the tajuna river in Spain}, author = {H C Peiretti and J T Liz and J M Mateos and A R Pérez and J R Martín and A P Caldentey}, isbn = {9789539542830}, year = {2007}, date = {2007-01-01}, booktitle = {Concrete Structures - Stimulators of Development, Proceedings of the fib Symposium Dubrovnik 2007}, pages = {955--962}, abstract = {This bridge is 2.000 m long and 140m high due to environmental requirements. Strict economical restrictions led to a bridge design that could he constructed in 36 months. The bridge has 14 spans of'40+3x70 + 150 +5x250 +1 50+2x70+40 m The deck has a very large 24.0 m wide, variable depth single-box cross section. The central part of the main span was designed with IJ-35 lightweight concrete whereas high performance 11-75 concrete was used at the piers. The main 250 m spans are to be built by the balanced cantilever method. The piers are very high, up to 125 m, with a hollow lx textgreater x cross section at the bottom and two shafts at the top, all made of high performance 11-75 concrete.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } This bridge is 2.000 m long and 140m high due to environmental requirements. Strict economical restrictions led to a bridge design that could he constructed in 36 months. The bridge has 14 spans of'40+3x70 + 150 +5x250 +1 50+2x70+40 m The deck has a very large 24.0 m wide, variable depth single-box cross section. The central part of the main span was designed with IJ-35 lightweight concrete whereas high performance 11-75 concrete was used at the piers. The main 250 m spans are to be built by the balanced cantilever method. The piers are very high, up to 125 m, with a hollow lx textgreater x cross section at the bottom and two shafts at the top, all made of high performance 11-75 concrete. |
2006 |
León González, J Reflections on bridge inspection | Reflexiones en torno a la inspección de puentes Journal Article Carreteras, 4 (147), pp. 7–26, 2006. @article{LeonGonzalez2006, title = {Reflections on bridge inspection | Reflexiones en torno a la inspección de puentes}, author = {J {León González}}, year = {2006}, date = {2006-01-01}, journal = {Carreteras}, volume = {4}, number = {147}, pages = {7--26}, abstract = {The great importance of a Bridge Management System, handled by structural engineers, is a matter of vindication in this article. Within this context, this paper is especifically dedicated to the role of the bridge inspection policy. Throughout an extensive overview of the different components of a bridge, both structural and non structural ones, and their peculiarities, special attention is paid to the fact that expertise and solid structural training is needed to carry out this task. Since such inspection must lead to a "damage index", the author claims for an affordable system to discriminate the signification of different types of damage, grouped into specialized catalogues that help the engineer to identify the damage, its origin and eventual concomitances, as well as its transcendence.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The great importance of a Bridge Management System, handled by structural engineers, is a matter of vindication in this article. Within this context, this paper is especifically dedicated to the role of the bridge inspection policy. Throughout an extensive overview of the different components of a bridge, both structural and non structural ones, and their peculiarities, special attention is paid to the fact that expertise and solid structural training is needed to carry out this task. Since such inspection must lead to a "damage index", the author claims for an affordable system to discriminate the signification of different types of damage, grouped into specialized catalogues that help the engineer to identify the damage, its origin and eventual concomitances, as well as its transcendence. |
Romo, J; Corres, H; Perez, A Seismic design of the Chacao Channel Bridge Journal Article Structures and Extreme Events. IABSE Symposium, 2006. @article{Romo2006, title = {Seismic design of the Chacao Channel Bridge}, author = {J Romo and H Corres and A Perez}, url = {http://gateway.webofknowledge.com/gateway/Gateway.cgi?GWVersion=2&SrcAuth=ORCID&SrcApp=OrcidOrg&DestLinkType=FullRecord&DestApp=INSPEC&KeyUT=INSPEC:9342319&KeyUID=INSPEC:9342319}, year = {2006}, date = {2006-01-01}, journal = {Structures and Extreme Events. IABSE Symposium}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L Salto del carnero railway bridge, Saragossa, Spain Journal Article Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 16 (3), pp. 200–203, 2006, ISSN: 10168664. @article{Tanner2006200, title = {Salto del carnero railway bridge, Saragossa, Spain}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-33747145322&doi=10.2749%2F101686606778026538&partnerID=40&md5=21471ea5341be3dd868f7c4e7a48dca6}, doi = {10.2749/101686606778026538}, issn = {10168664}, year = {2006}, date = {2006-01-01}, journal = {Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, volume = {16}, number = {3}, pages = {200--203}, abstract = {The ideas underlying the conceptual design for the Salto del Carnero railway bridge at Saragossa, Spain, with respect to the specific boundary conditions, are described. This overpass, situated only one hundred meters from Delicias station, spans eight railway tracks, including the Madrid-Barcelona high-speed railway and regional and commuter train tracks. The single track carried by the bridge, exclusively for shunting purposes, is subject to a 4,6 m horizontal clearances requirement. The bridge was designed to the form-following-function principle, according to which structural form stems from functional requirements and site constraints. The total bridge length of 124 m is divided into two outer spans, each 25 m long, and two inner spans measuring 37 m each. The construction of this bridge indicate that the success of a structural design depends on fluent communication between the structural engineer and the owner or its representatives throughout all the design stages.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The ideas underlying the conceptual design for the Salto del Carnero railway bridge at Saragossa, Spain, with respect to the specific boundary conditions, are described. This overpass, situated only one hundred meters from Delicias station, spans eight railway tracks, including the Madrid-Barcelona high-speed railway and regional and commuter train tracks. The single track carried by the bridge, exclusively for shunting purposes, is subject to a 4,6 m horizontal clearances requirement. The bridge was designed to the form-following-function principle, according to which structural form stems from functional requirements and site constraints. The total bridge length of 124 m is divided into two outer spans, each 25 m long, and two inner spans measuring 37 m each. The construction of this bridge indicate that the success of a structural design depends on fluent communication between the structural engineer and the owner or its representatives throughout all the design stages. |
2005 |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L Widening of the elche de la sierra arch Bridge, Spain Journal Article Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE), 15 (3), pp. 148–150, 2005, ISSN: 10168664. @article{Tanner2005148, title = {Widening of the elche de la sierra arch Bridge, Spain}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-23844444608&partnerID=40&md5=83e0f8111d2629077fb15335ede1c656}, issn = {10168664}, year = {2005}, date = {2005-01-01}, journal = {Structural Engineering International: Journal of the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering (IABSE)}, volume = {15}, number = {3}, pages = {148--150}, abstract = {The assessment of Elche de la Sierra, an existing arch bridge over 70 years old, conducted when the need arose to widen its deck. The conceptual design for widening the arch bridge involved the construction of a new cast-in-place concrete slab. The need to ensure the composite action of the existing and new concretes in the widened deck slab and to guarantee due performance under service conditions, especially to attenuate cracking in the new concrete cast against the existing deck, called for a series of measures. The challenge was to verify whether the existing structure would be reliable and fit for use with no futher strengthening under the new service conditions.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The assessment of Elche de la Sierra, an existing arch bridge over 70 years old, conducted when the need arose to widen its deck. The conceptual design for widening the arch bridge involved the construction of a new cast-in-place concrete slab. The need to ensure the composite action of the existing and new concretes in the widened deck slab and to guarantee due performance under service conditions, especially to attenuate cracking in the new concrete cast against the existing deck, called for a series of measures. The challenge was to verify whether the existing structure would be reliable and fit for use with no futher strengthening under the new service conditions. |
2004 |
Peiretti, H C; Martín, J R; Caldentey, A P Railway bridges. Design basis, concepts and possibilities | Puentes de ferrocarril. Bases de proyecto, çoncepción y posibilidades tipológicas Journal Article Revista de Obras Publicas, 151 (3445), pp. 91–102, 2004. @article{Peiretti2004a, title = {Railway bridges. Design basis, concepts and possibilities | Puentes de ferrocarril. Bases de proyecto, çoncepción y posibilidades tipológicas}, author = {H C Peiretti and J R Martín and A P Caldentey}, year = {2004}, date = {2004-01-01}, journal = {Revista de Obras Publicas}, volume = {151}, number = {3445}, pages = {91--102}, abstract = {The railway sector has undergone considerable change over recent decades as a result of high speed rail lines. The need to build new railway lines has served as the driving force behind technological innovation and the new codes regarding railway bridges. The solutions employed in these bridges have to take account of the presence of greater loading and comply with the strict functional requirements demanded of high speed traffic. Under normal spans of between 20 and 70 m, post-stressed constant depth beam solutions tend to be more commonly employed though composite solutions are also very much to the fore in other European countries. However, one important aspect when conceiving the original structure is undoubtedly the longitudinal arrangement of the structure and the method of transferring horizontal loads to the foundations and this particular problem is the subject of study in the present article.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The railway sector has undergone considerable change over recent decades as a result of high speed rail lines. The need to build new railway lines has served as the driving force behind technological innovation and the new codes regarding railway bridges. The solutions employed in these bridges have to take account of the presence of greater loading and comply with the strict functional requirements demanded of high speed traffic. Under normal spans of between 20 and 70 m, post-stressed constant depth beam solutions tend to be more commonly employed though composite solutions are also very much to the fore in other European countries. However, one important aspect when conceiving the original structure is undoubtedly the longitudinal arrangement of the structure and the method of transferring horizontal loads to the foundations and this particular problem is the subject of study in the present article. |
2003 |
Romo, J; Corres, H; Pérez, A; Granda, L Chacao Channel Bridge. Seismic design basis and seismic design Inproceedings Proceedings of the fib Symposium 2003: Concrete Structures in Seismic Regions, pp. 420–421, 2003. @inproceedings{Romo2003a, title = {Chacao Channel Bridge. Seismic design basis and seismic design}, author = {J Romo and H Corres and A Pérez and L Granda}, year = {2003}, date = {2003-01-01}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the fib Symposium 2003: Concrete Structures in Seismic Regions}, pages = {420--421}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } |
Corres, H; Romo, J; Caldentey, A P Some contributions to new ideas and design concepts in the design of bridges Inproceedings Role of Concrete Bridges in Sustainable Development - Proceedings of the International Symposium - Celebrating Concrete: People and Practice, pp. 95–108, 2003, ISBN: 9780727732484. @inproceedings{Corres2003, title = {Some contributions to new ideas and design concepts in the design of bridges}, author = {H Corres and J Romo and A P Caldentey}, isbn = {9780727732484}, year = {2003}, date = {2003-01-01}, booktitle = {Role of Concrete Bridges in Sustainable Development - Proceedings of the International Symposium - Celebrating Concrete: People and Practice}, pages = {95--108}, abstract = {In the design of bridges as well as that of any other type of structure the solution of a problem is implicit. For any such problem there are, on the one hand, specific conditions which must be fulfilled and, on the other, an infinite number of possible solutions. The search for the optimal solution, generally, is not the result of sudden inspiration but the result of a slow approximation to the problem, in order to attain a detailed understanding of the same, and of the rigorous, conscientious and deep consideration of all the available possibilities, including the more creative, unedited and innovative ones. In this process, the deep knowledge, the previous experience and the personal talent are crucial with respect to the final result. This process, which can hardly be explained in words, is what is known as conceptual design. It is part of the trade qualities which a good structural engineer should have. It requires not only a solid education and the capacity to have broad view of things at University level, but also, the learning provided by professional practice, directed by good teachers and a humble and self-sacrificing attitude. Creating a new idea, daring to give liberty to imagination requires a first experience of true creation. With the above conditions, creation will come naturally when confronting each problem. It is necessary to practice this methodology with each new project, independently of its size, its importance or its impact. What is important is to make a great project out of every engineering problem to be solved. Any project, be it, ever so modest, gives opportunity to produce good and creative engineering. In this paper these ideas are discussed, analysing the process through the experience of developing a number of specific projects.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } In the design of bridges as well as that of any other type of structure the solution of a problem is implicit. For any such problem there are, on the one hand, specific conditions which must be fulfilled and, on the other, an infinite number of possible solutions. The search for the optimal solution, generally, is not the result of sudden inspiration but the result of a slow approximation to the problem, in order to attain a detailed understanding of the same, and of the rigorous, conscientious and deep consideration of all the available possibilities, including the more creative, unedited and innovative ones. In this process, the deep knowledge, the previous experience and the personal talent are crucial with respect to the final result. This process, which can hardly be explained in words, is what is known as conceptual design. It is part of the trade qualities which a good structural engineer should have. It requires not only a solid education and the capacity to have broad view of things at University level, but also, the learning provided by professional practice, directed by good teachers and a humble and self-sacrificing attitude. Creating a new idea, daring to give liberty to imagination requires a first experience of true creation. With the above conditions, creation will come naturally when confronting each problem. It is necessary to practice this methodology with each new project, independently of its size, its importance or its impact. What is important is to make a great project out of every engineering problem to be solved. Any project, be it, ever so modest, gives opportunity to produce good and creative engineering. In this paper these ideas are discussed, analysing the process through the experience of developing a number of specific projects. |
2001 |
Corres Peiretti, H; Pérez Caldentey, A Composite truss bridge decks | Tableros de celosías mixtas Journal Article Revista de Obras Publicas, 148 (3416), pp. 13–37, 2001. @article{CorresPeiretti2001, title = {Composite truss bridge decks | Tableros de celosías mixtas}, author = {H {Corres Peiretti} and A {Pérez Caldentey}}, year = {2001}, date = {2001-01-01}, journal = {Revista de Obras Publicas}, volume = {148}, number = {3416}, pages = {13--37}, abstract = {This article analyzes the problems of detailing, design, and construction of composite truss decks. With regards to detailing special emphasis is placed on the form of joints employed in this type of structure and a description is given of several different solutions which have been used to tackle this problem in recently built Spanish bridges. Moving on to the design aspects, the article underlines the importance of the axial-moment-shear interaction in composite trusses, particularly in the upper chord which is subject to heavy local bending due to traffic loads. The article also considers, in design terms, the example of the Cavalls Bridge in Valencia and several considerations are made regarding the combination of truss structures with external prestressing and the criteria which should be followed to design the prestress force in this type of structure, which to a certain extent falls midway between the external prestressing of a concrete box sections and the prestressing of a cable stayed bridge. The article concludes with an analysis of the different construction procedures that have been employed in truss structures and emphasises the many building possibilities that have been opened up today by modern technique.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } This article analyzes the problems of detailing, design, and construction of composite truss decks. With regards to detailing special emphasis is placed on the form of joints employed in this type of structure and a description is given of several different solutions which have been used to tackle this problem in recently built Spanish bridges. Moving on to the design aspects, the article underlines the importance of the axial-moment-shear interaction in composite trusses, particularly in the upper chord which is subject to heavy local bending due to traffic loads. The article also considers, in design terms, the example of the Cavalls Bridge in Valencia and several considerations are made regarding the combination of truss structures with external prestressing and the criteria which should be followed to design the prestress force in this type of structure, which to a certain extent falls midway between the external prestressing of a concrete box sections and the prestressing of a cable stayed bridge. The article concludes with an analysis of the different construction procedures that have been employed in truss structures and emphasises the many building possibilities that have been opened up today by modern technique. |
2000 |
Tanner, P; Bellod, J L; Sanz, M; Gutsch, A -W; Barthel, T Stahlbau, 69 (9), pp. 714–718, 2000, ISSN: 00389145. @article{Tanner2000714, title = {Reduction of risks during assembly risks with on-line measurements at the Spanish EXPO-pavilion [Verringerung der Montagerisiken durch baubegleitende Messungen am spanischen EXPO-Pavillon]}, author = {P Tanner and J L Bellod and M Sanz and A -W Gutsch and T Barthel}, url = {https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-0034272317&partnerID=40&md5=5506d0adc24d0752af941660f7cadaaa}, issn = {00389145}, year = {2000}, date = {2000-01-01}, journal = {Stahlbau}, volume = {69}, number = {9}, pages = {714--718}, publisher = {Ernst & Sohn, Berlin, Germany}, abstract = {The construction of the Spanish pavilion for the Expo 2000 required very careful planning, bearing in mind the complex interactions between the geometry, functionality, structural concept and construction materials used. The need for the structure to be dismountable advised the extensive use of prefabrication techniques. Using a coherent structural concept, in which all the elements contribute to the overall stability of the system, a completely prefabricated and dismountable structure of great robustness has been achieved. A detailed structural analysis allowed the sensitivity of the structural behaviour towards different parameters to be identified, particularly during the application of the prestressing forces. Finally, the structure was monitored with a view to keeping these parameters within allowable limits.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } The construction of the Spanish pavilion for the Expo 2000 required very careful planning, bearing in mind the complex interactions between the geometry, functionality, structural concept and construction materials used. The need for the structure to be dismountable advised the extensive use of prefabrication techniques. Using a coherent structural concept, in which all the elements contribute to the overall stability of the system, a completely prefabricated and dismountable structure of great robustness has been achieved. A detailed structural analysis allowed the sensitivity of the structural behaviour towards different parameters to be identified, particularly during the application of the prestressing forces. Finally, the structure was monitored with a view to keeping these parameters within allowable limits. |
1997 |
Casati, M J; Diez, M; Galvez, J C; Leon, J Study of sensitivity of structural analysis on the vertical section through the main nave of the Cathedral of Leon Inproceedings International Series on Advances in Architecture, pp. 179–189, 1997. @inproceedings{Casati1997, title = {Study of sensitivity of structural analysis on the vertical section through the main nave of the Cathedral of Leon}, author = {M J Casati and M Diez and J C Galvez and J Leon}, year = {1997}, date = {1997-01-01}, booktitle = {International Series on Advances in Architecture}, volume = {3}, pages = {179--189}, abstract = {A sensitivity analysis about the influence of the E-modulus distribution, differential settlements, variation in geometrical definition, distribution of stone densities, etc, (related to the vertical section through the main nave) is here presented. The purpose is to calibrate the importance of such variables in the relevant parameters (internal forces, stresses and displacements) in order to have consistent criteria to define what to monitorize and where to install measurement devices in strategic places. This should lead to reduce monitoring cost and to deep in the knowledge of the structural behaviour of the monument.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } A sensitivity analysis about the influence of the E-modulus distribution, differential settlements, variation in geometrical definition, distribution of stone densities, etc, (related to the vertical section through the main nave) is here presented. The purpose is to calibrate the importance of such variables in the relevant parameters (internal forces, stresses and displacements) in order to have consistent criteria to define what to monitorize and where to install measurement devices in strategic places. This should lead to reduce monitoring cost and to deep in the knowledge of the structural behaviour of the monument. |
1988 |
Planas, J; Corres, H; Elices, M Behaviour at cryogenic temperatures of tendon anchorages for prestressing concrete Journal Article Materials and Structures, 21 (4), pp. 278–285, 1988. @article{Planas1988, title = {Behaviour at cryogenic temperatures of tendon anchorages for prestressing concrete}, author = {J Planas and H Corres and M Elices}, doi = {10.1007/BF02481826}, year = {1988}, date = {1988-01-01}, journal = {Materials and Structures}, volume = {21}, number = {4}, pages = {278--285}, abstract = {Tendon anchorages are sensitive zones where fractures may be produced and this risk may be increased at low temperatures. No international standards for tendon anchorages at low temperatures have yet been developed. This paper aims at two objectives: to furnish information on the behaviour, at low temperatures, of two commercial tendon anchorage systems and to make some proposals, as well as related testing procedures, for pre-stressing systems intended for cryogenic applications. textcopyright 1988 RILEM.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Tendon anchorages are sensitive zones where fractures may be produced and this risk may be increased at low temperatures. No international standards for tendon anchorages at low temperatures have yet been developed. This paper aims at two objectives: to furnish information on the behaviour, at low temperatures, of two commercial tendon anchorage systems and to make some proposals, as well as related testing procedures, for pre-stressing systems intended for cryogenic applications. textcopyright 1988 RILEM. |
1986 |
Elices, M; Planas, J; Corres, H Thermal deformation of loaded concrete at low temperatures, 2: Transverse deformation Journal Article Cement and Concrete Research, 16 (5), pp. 741–748, 1986. @article{Elices1986, title = {Thermal deformation of loaded concrete at low temperatures, 2: Transverse deformation}, author = {M Elices and J Planas and H Corres}, doi = {10.1016/0008-8846(86)90048-7}, year = {1986}, date = {1986-01-01}, journal = {Cement and Concrete Research}, volume = {16}, number = {5}, pages = {741--748}, abstract = {Transverse thermal deformation of concrete cylinders has been measured during a thermal cycle, up to -90°C. Oven dry concrete shows an almost linear, reversible and isotropic behaviour. Load-free water-saturated concrete exhibits a complex strain behaviour, characterized by dilatation during cooling (from -10°C to -60°C) and an irreversible expansion after reheating. Longitudinal loading (15 MPa) enhances the aforementioned behaviour. A qualitative explanation of such effects is outlined. textcopyright 1986.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Transverse thermal deformation of concrete cylinders has been measured during a thermal cycle, up to -90°C. Oven dry concrete shows an almost linear, reversible and isotropic behaviour. Load-free water-saturated concrete exhibits a complex strain behaviour, characterized by dilatation during cooling (from -10°C to -60°C) and an irreversible expansion after reheating. Longitudinal loading (15 MPa) enhances the aforementioned behaviour. A qualitative explanation of such effects is outlined. textcopyright 1986. |
Corres, H; Elices, M; Planas, J Thermal deformation of loaded concrete at low temperatures. 3: Lightweight concrete Journal Article Cement and Concrete Research, 16 (6), pp. 845–852, 1986. @article{Corres1986, title = {Thermal deformation of loaded concrete at low temperatures. 3: Lightweight concrete}, author = {H Corres and M Elices and J Planas}, doi = {10.1016/0008-8846(86)90007-4}, year = {1986}, date = {1986-01-01}, journal = {Cement and Concrete Research}, volume = {16}, number = {6}, pages = {845--852}, abstract = {Longitudinal and transverse thermal deformation has been measured on lightweight concrete cylinders during a thermal cycle, from room temperature up to -90°C. Oven-dry samples show an almost linear, isotropic, reversible and load independent dilatational behaviour. Water-saturated samples behave in a different way; when load-free, thermal deformation is nearly isotropic, although highly non linear (between -10°C and -60°C) and ending with an irreversible expansion. When axially loaded (10 MPa), lightweight concrete shows a strongly anisotropic behaviour. Volumetric thermal deformation, for a given moisture content, does not seems to depend on applied load. textcopyright 1986.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Longitudinal and transverse thermal deformation has been measured on lightweight concrete cylinders during a thermal cycle, from room temperature up to -90°C. Oven-dry samples show an almost linear, isotropic, reversible and load independent dilatational behaviour. Water-saturated samples behave in a different way; when load-free, thermal deformation is nearly isotropic, although highly non linear (between -10°C and -60°C) and ending with an irreversible expansion. When axially loaded (10 MPa), lightweight concrete shows a strongly anisotropic behaviour. Volumetric thermal deformation, for a given moisture content, does not seems to depend on applied load. textcopyright 1986. |
1984 |
Planas, J; Corres, H; Elices, M; Chueca, R Thermal deformation of loaded concrete during thermal cycles from 20°C to -165°C Journal Article Cement and Concrete Research, 14 (5), pp. 639–644, 1984. @article{Planas1984, title = {Thermal deformation of loaded concrete during thermal cycles from 20°C to -165°C}, author = {J Planas and H Corres and M Elices and R Chueca}, doi = {10.1016/0008-8846(84)90026-7}, year = {1984}, date = {1984-01-01}, journal = {Cement and Concrete Research}, volume = {14}, number = {5}, pages = {639--644}, abstract = {Thermal deformation of concrete samples has been measured. Unloaded water-saturated concrete exhibits a complex strain behaviour during thermal cycles, characterized by dilatation cooling and an irreversible expansion reheating. Loaded water-saturated concrete behaves in a different way. The transition region id reversed -with respect to unloaded samples- and almost dissapears, when compressive stress of 15 MPa is applied. Also an irreversible compressive deformation is bound after reheating. A qualitative explanation of such effects, assuming that microcracking is the dominant deformation mechanism in the transition range, is offered. Further research is needed along this direction. textcopyright 1984.}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {article} } Thermal deformation of concrete samples has been measured. Unloaded water-saturated concrete exhibits a complex strain behaviour during thermal cycles, characterized by dilatation cooling and an irreversible expansion reheating. Loaded water-saturated concrete behaves in a different way. The transition region id reversed -with respect to unloaded samples- and almost dissapears, when compressive stress of 15 MPa is applied. Also an irreversible compressive deformation is bound after reheating. A qualitative explanation of such effects, assuming that microcracking is the dominant deformation mechanism in the transition range, is offered. Further research is needed along this direction. textcopyright 1984. |
1983 |
Corres, H; Planas, J; Elices, M; Sanchez-Galvez, V; Chueca, R BEHAVIOUR OF TENDON-ANCHORAGE ASSEMBLIES UNDER CRYOGENIC CONDITIONS. Inproceedings 1983. @inproceedings{Corres1983, title = {BEHAVIOUR OF TENDON-ANCHORAGE ASSEMBLIES UNDER CRYOGENIC CONDITIONS.}, author = {H Corres and J Planas and M Elices and V Sanchez-Galvez and R Chueca}, year = {1983}, date = {1983-01-01}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } |
Planas, J; Corres, H; Chueca, R; Elices, M; Sanchez-Galvez, V INFLUENCE OF LOAD ON THERMAL DEFORMATION OF CONCRETE DURING COOLING DOWN. Inproceedings 1983. @inproceedings{Planas1983a, title = {INFLUENCE OF LOAD ON THERMAL DEFORMATION OF CONCRETE DURING COOLING DOWN.}, author = {J Planas and H Corres and R Chueca and M Elices and V Sanchez-Galvez}, year = {1983}, date = {1983-01-01}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } |
Planas, J; Corres, H; Elices, M; Sanchez-Galvez, V TENSILE TESTS OF STEEL AT LOW TEMPERATURES. PROBLEMS DUE TO NONUNIFORMITY IN THE TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION ALONG THE SPECIMEN. Inproceedings 1983. @inproceedings{Planas1983b, title = {TENSILE TESTS OF STEEL AT LOW TEMPERATURES. PROBLEMS DUE TO NONUNIFORMITY IN THE TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION ALONG THE SPECIMEN.}, author = {J Planas and H Corres and M Elices and V Sanchez-Galvez}, year = {1983}, date = {1983-01-01}, keywords = {}, pubstate = {published}, tppubtype = {inproceedings} } |


